Vibrating Fluid Bed Dryer Manufacturer
-

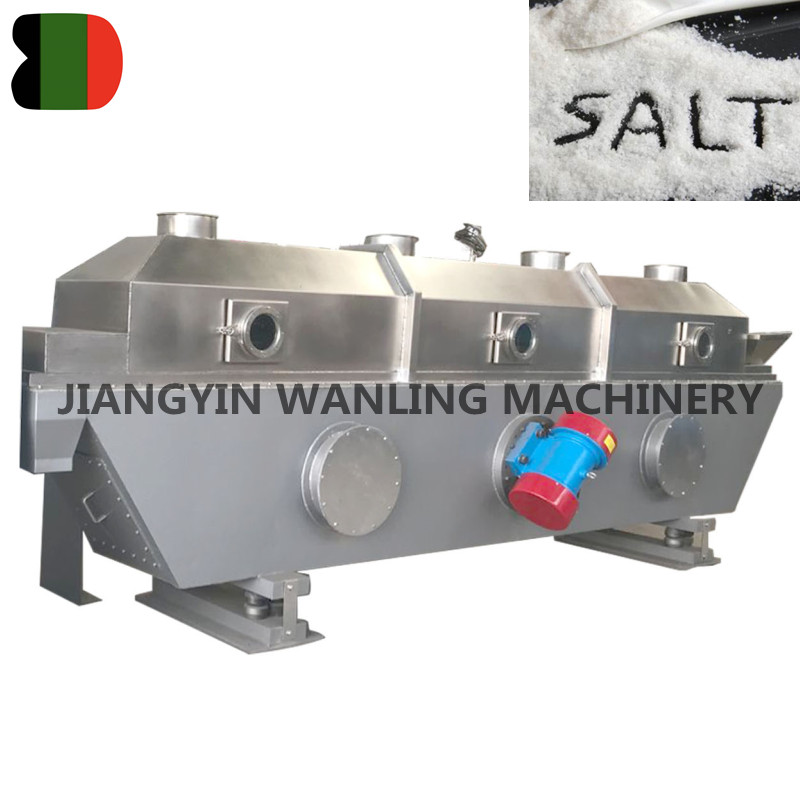
ZG Plastic Vibrating Fluid Bed Dryer Machine
This type Vibration Fluid Bed Dryer is suitable for drying, cooling and humidifying of materials in various industries, such as chemical ind... -

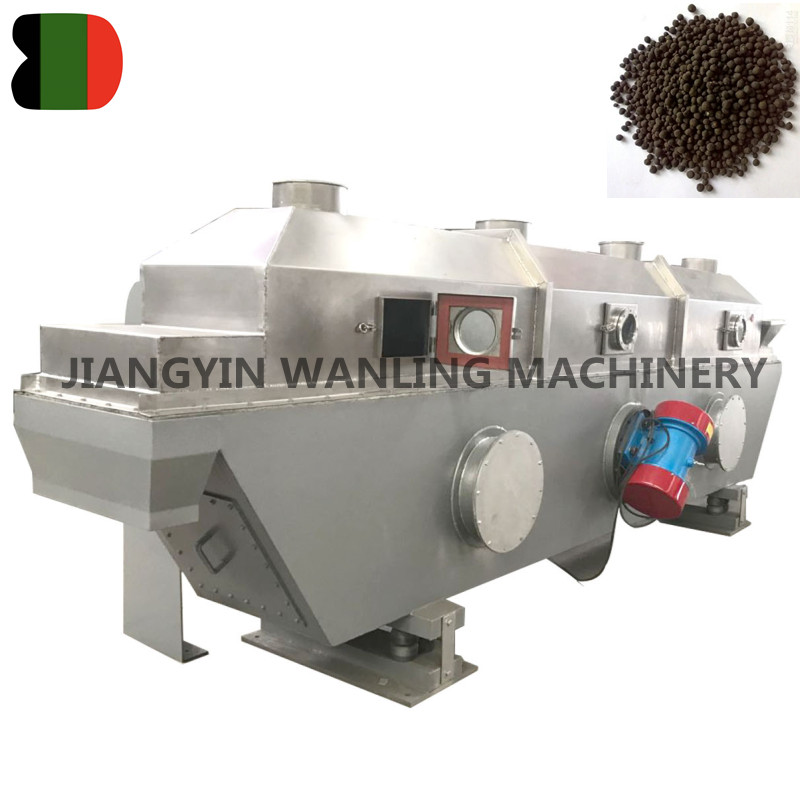
ZG Industrial Horizontal Type Vibrating Fluid Bed Dryer Machine
FEATURES Energy efficient with potential savings of 30-60% compared to traditional dryers. Enclosed design prevents cross-contamination and ... -

ZG industrial vibrating fluid bed dryer
The industrial vibrating fluid bed dryer can dry powder and granules, it is horizontal type drying machine. The drying machine can work cont...
Vibrating fluid bed dryer is a new type of fluidized high-efficiency drying equipment suitable for drying granular and powdered materials. It has advantages such as easy operation, energy conservation, and environmental protection. A vibrating fluidized bed is a new type of drying device that applies a specific vibration source to a regular fluidized bed dryer. The fluidized bed dryer is suitable for drying, cooling, and humidifying various granular material crystals and powder particle mixtures. It is widely used in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.

About Us
Honor
-
 Honor
Honor -
 CE
CE
News
-
Industry News 2026-01-20
Introduction to Fluid Bed Granulators in Powder Processing Fluid bed granulators have become a cruci...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-12
Introduction to Tray Dryers Tray dryers are widely used industrial drying machines designed for dryi...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-06
Introduction to Spice Grinding Machines Grinding machines for spices are essential equipment for bot...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-04
Introduction to Industrial Drying Methods Drying is a critical process in pharmaceutical, chemical, ...
View More
Industry Knowledge Expansion
Can a vibrating fluid bed dryer be integrated into existing production lines easily?
Space Requirements: Evaluate whether there is sufficient space within the existing production line layout to accommodate the vibrating fluid bed dryer. Consider factors such as clearance for maintenance, access to utilities (e.g., electricity, gas), and ventilation requirements.
Compatibility with Existing Equipment: Assess whether the vibrating fluid bed dryer can seamlessly integrate with other equipment in the production line, such as feeders, conveyors, and packaging machinery. Compatibility ensures smooth material flow and process continuity.
Utility Connections: Ensure that necessary utility connections, such as electricity, compressed air, and exhaust systems, are available near the intended installation site. If modifications or additional connections are required, plan and coordinate with relevant stakeholders.
Material Handling: Determine how materials will be fed into and discharged from the vibrating fluid bed dryer. Depending on the production process, adjustments or additions to material handling systems may be necessary to facilitate seamless integration.
Control and Automation: Assess the compatibility of the vibrating fluid bed dryer's control system with existing process control infrastructure. Integration may involve interfacing the dryer's control system with centralized control systems or programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in the production line.
Training and Support: Provide training for operators and maintenance personnel on the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the vibrating fluid bed dryer. Access to technical support from the equipment manufacturer can also facilitate smooth integration and ongoing support.
How does a vibrating fluid bed dryer differ from traditional fluidized bed dryers?
Vibration: In a vibrating fluid bed dryer, a specific vibration source is applied to the fluidized bed. This vibration enhances the fluidization of the material particles, promoting better mixing and heat transfer. Traditional fluidized bed dryers typically rely solely on fluidizing air to suspend and agitate the material.
Enhanced Heat and Mass Transfer: The application of vibration in a vibrating fluid bed dryer facilitates improved heat and mass transfer between the drying medium (usually air or gas) and the material being processed. This results in more efficient drying with shorter residence times and potentially lower energy consumption compared to traditional fluidized bed dryers.
Uniformity of Drying: The vibration in a vibrating fluid bed dryer helps to ensure more uniform drying of the material throughout the bed. This uniformity is particularly beneficial for materials with varying particle sizes or moisture content, as it helps prevent localized drying or overheating.
Control and Flexibility: Vibrating fluid bed dryers often offer greater control and flexibility in terms of adjusting process parameters such as vibration intensity, airflow rate, and temperature. This enables operators to optimize drying conditions for different materials and production requirements.


 Español
Español