Content
- 1 What Is a Fluid Bed Dryer
- 2 Principles of Fluid Bed Drying and Fluidized Bed Drying
- 3 Vertical Fluidized Bed Drying Systems
- 4 Vertical Blending Fluidized Bed Drying
- 5 Comparison of Fluid Bed Dryers and Conventional Drying Methods
- 6 Common Materials Processed Using Fluidized Bed Drying
- 7 Why Fluid Bed Dryers Are Widely Adopted
What Is a Fluid Bed Dryer
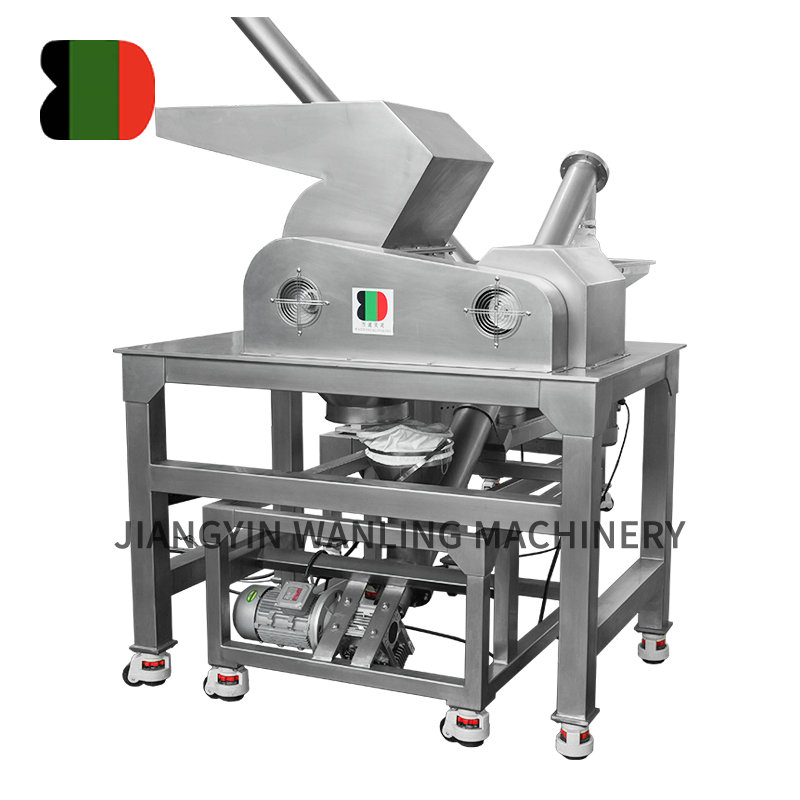
A fluid bed dryer is an industrial drying system that removes moisture from powders, granules, or particulate materials by suspending them in a stream of heated air. When air flows upward through a perforated distributor plate at sufficient velocity, solid particles become fluidized, behaving similarly to a boiling liquid. This fluid-like movement allows uniform heat transfer and efficient moisture evaporation throughout the material bed.
Fluid bed dryers are widely used in pharmaceutical, chemical, food, and material processing industries because they provide controlled drying conditions, consistent product quality, and relatively short processing times compared with static drying methods.
Principles of Fluid Bed Drying and Fluidized Bed Drying
Fluid bed drying, also referred to as fluidized bed drying, is based on the interaction between solid particles and a flowing gas medium. As hot air passes through the material, it transfers thermal energy to the particles while simultaneously carrying away evaporated moisture. Because each particle is surrounded by air, heat and mass transfer occur evenly across the entire batch.
This drying mechanism minimizes temperature gradients within the product bed and reduces the risk of localized overheating. As a result, fluidized bed drying is suitable for materials that require gentle yet efficient moisture removal.
Key Factors Influencing Drying Performance
Several operational parameters directly affect the efficiency and consistency of fluid bed drying. Proper adjustment of these factors helps achieve target moisture levels while maintaining product integrity.
- Air temperature and humidity, which determine drying potential
- Airflow velocity, influencing the stability of fluidization
- Particle size and density, affecting fluidization behavior
- Bed depth and load volume, impacting heat transfer efficiency
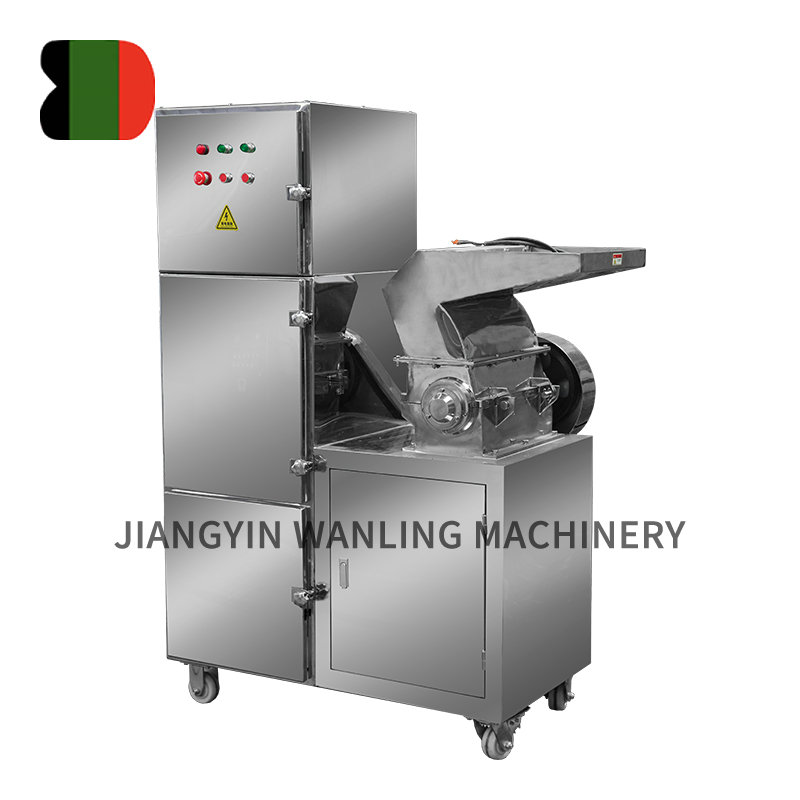
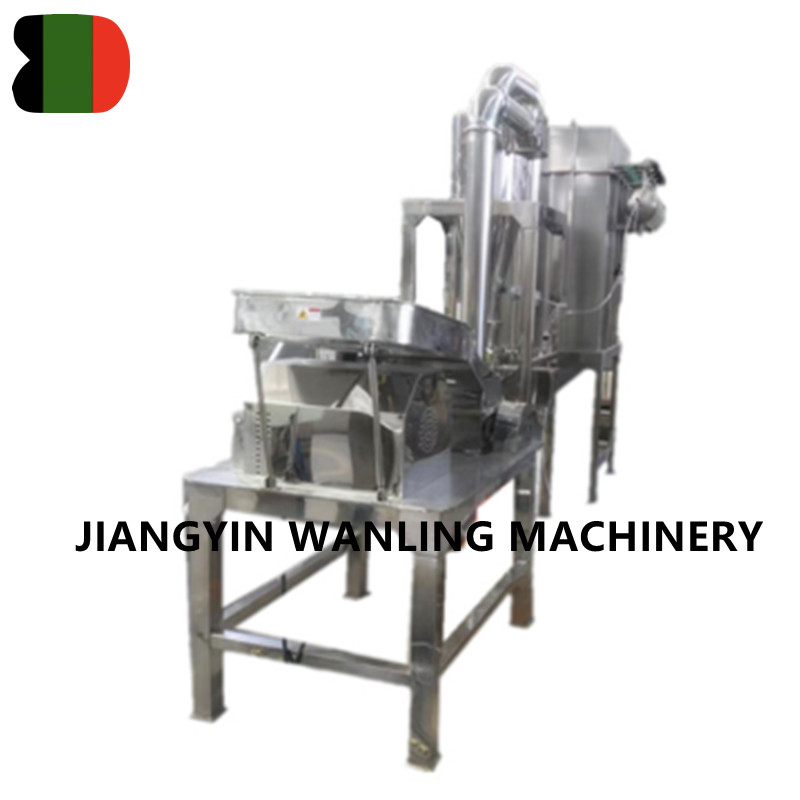
Vertical Fluidized Bed Drying Systems
Vertical fluidized bed drying systems are designed with an upright chamber configuration, allowing air to flow vertically from the bottom to the top of the material bed. This structure promotes uniform fluidization across the entire cross-section of the dryer, making it suitable for batch or continuous drying processes.
The vertical design supports efficient use of floor space and enables easier integration with upstream and downstream equipment such as feeders, blenders, or discharge units.
Operational Advantages of Vertical Configurations
Vertical fluidized bed drying offers several operational benefits, particularly in controlled manufacturing environments.
- Consistent air distribution for uniform drying results
- Compact footprint compared with horizontal systems
- Easier cleaning and inspection access
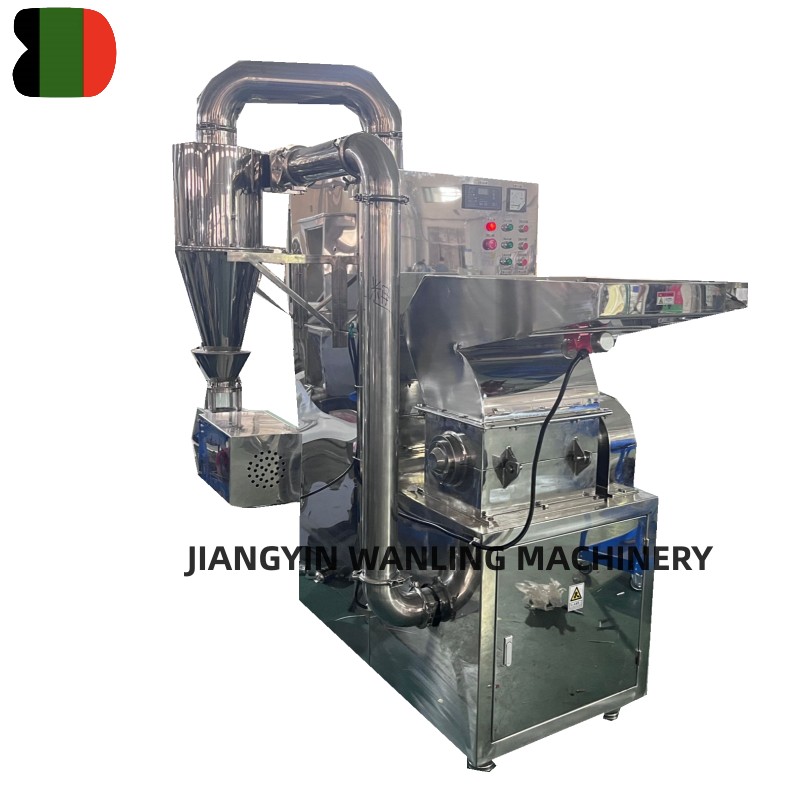
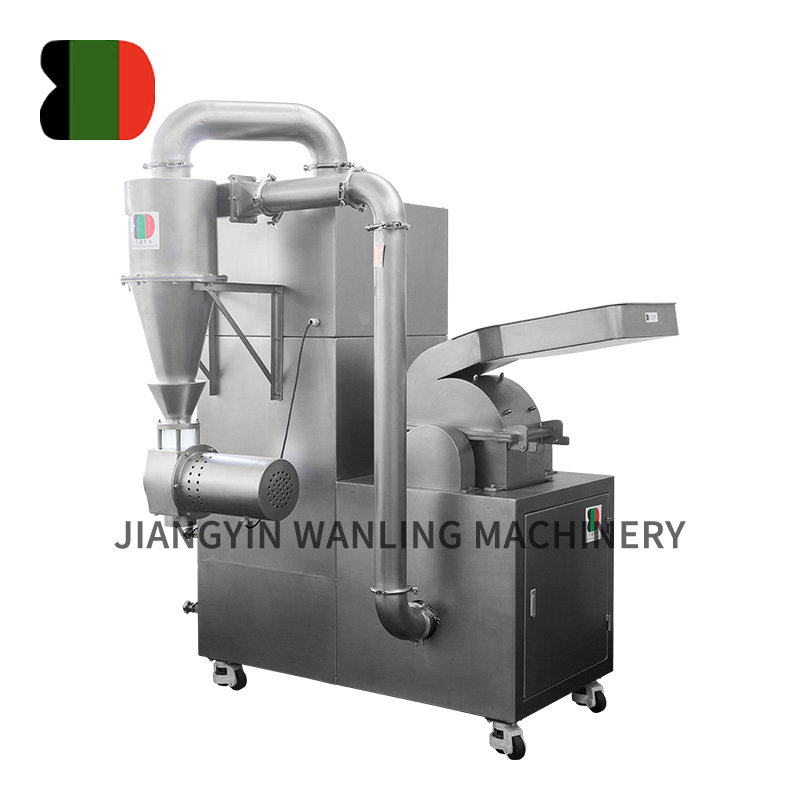
Vertical Blending Fluidized Bed Drying
Vertical blending fluidized bed drying combines drying and mixing functions within a single processing unit. In this configuration, the fluidization airflow not only dries the material but also promotes continuous particle movement, achieving effective blending without the need for separate mixing equipment.
This integrated approach is particularly useful for formulations that require uniform distribution of components or consistent moisture content throughout the batch. The blending effect reduces segregation and enhances overall process efficiency.
Applications Requiring Simultaneous Drying and Blending
Industries that handle multi-component powders or granules often rely on vertical blending fluidized bed drying to streamline production workflows.
- Pharmaceutical granules requiring uniform moisture levels
- Food ingredients with controlled particle distribution
- Chemical powders where homogeneity affects performance
Comparison of Fluid Bed Dryers and Conventional Drying Methods
Selecting a drying system requires understanding how fluid bed dryers differ from conventional alternatives. Fluidized bed drying emphasizes efficiency and uniformity, while traditional methods may rely on static heat transfer.
| Aspect | Fluid Bed Dryers | Conventional Dryers |
| Heat Transfer | Uniform and efficient | Often uneven |
| Drying Time | Relatively short | Longer processing cycles |
| Product Consistency | High consistency | Variable results |
Common Materials Processed Using Fluidized Bed Drying
Fluidized bed drying is suitable for a wide range of materials, provided that particle size and density allow stable fluidization. Proper system design ensures gentle handling while maintaining drying efficiency.
Typical materials include pharmaceutical granules, food powders, chemical intermediates, and specialty materials that require controlled moisture reduction without mechanical stress.
Why Fluid Bed Dryers Are Widely Adopted
Fluid bed dryers continue to be widely adopted because they offer a combination of efficiency, flexibility, and process control. Whether used for standard fluid bed drying, vertical fluidized bed drying, or vertical blending fluidized bed drying, these systems support consistent product quality and scalable production.
By enabling uniform heat transfer and adaptable process integration, fluidized bed drying technology remains a practical solution for industries seeking reliable and repeatable drying performance.


 Español
Español