Content
- 1 Introduction to Rotary Airlock Valves
- 2 Basic Structure of a Rotary Airlock Valve
- 3 Working Principle of a Rotary Airlock Valve
- 4 Key Operational Considerations
- 5 Types of Rotary Airlock Valves
- 6 Design Considerations
- 7 Applications Across Industries
- 8 Table of Key Specifications
- 9 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- 10 Conclusion
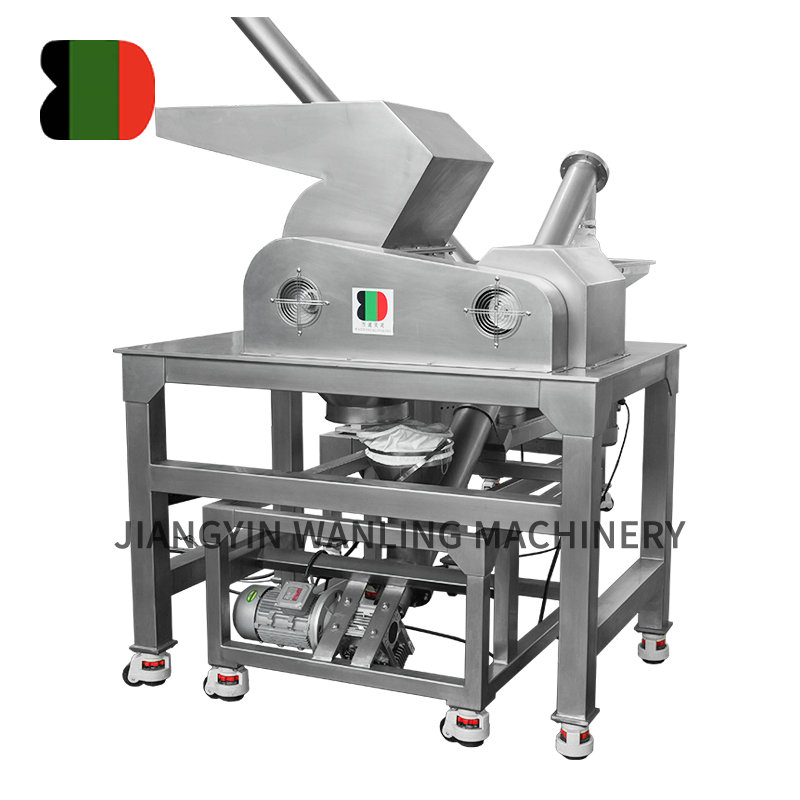
Introduction to Rotary Airlock Valves
Rotary airlock valves are key components in bulk material handling systems, widely used in industries such as cement, food processing, chemical, and pharmaceuticals. Their primary function is to maintain a consistent material flow while isolating different pressure zones in pneumatic conveying systems. Understanding the working principle of rotary airlock valves is essential for efficient operation, proper maintenance, and selection of the right valve for specific applications.
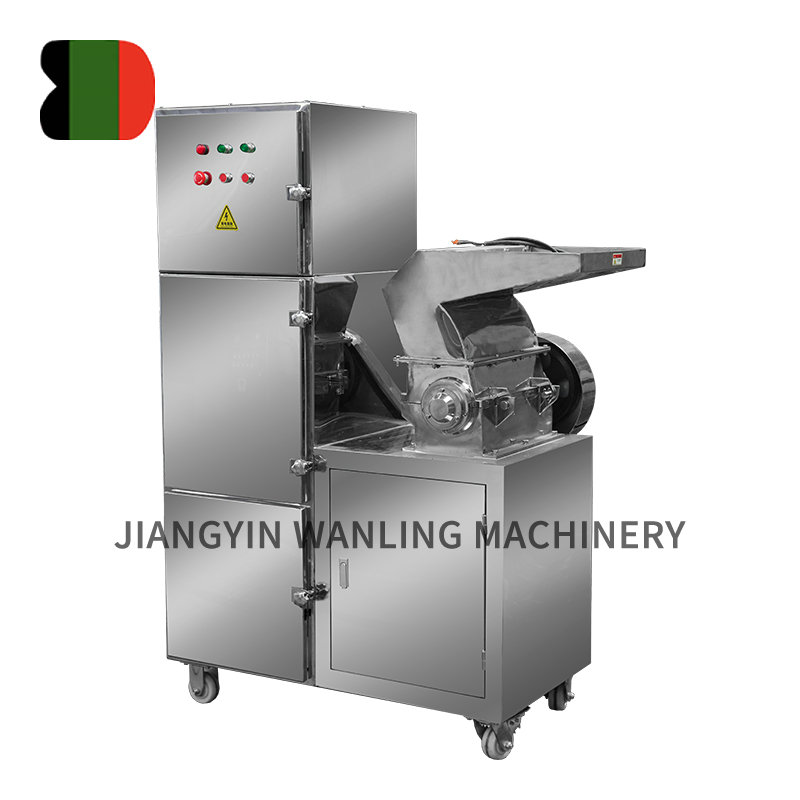
Basic Structure of a Rotary Airlock Valve
A rotary airlock valve consists of several core components that work together to achieve continuous material flow and pressure isolation:
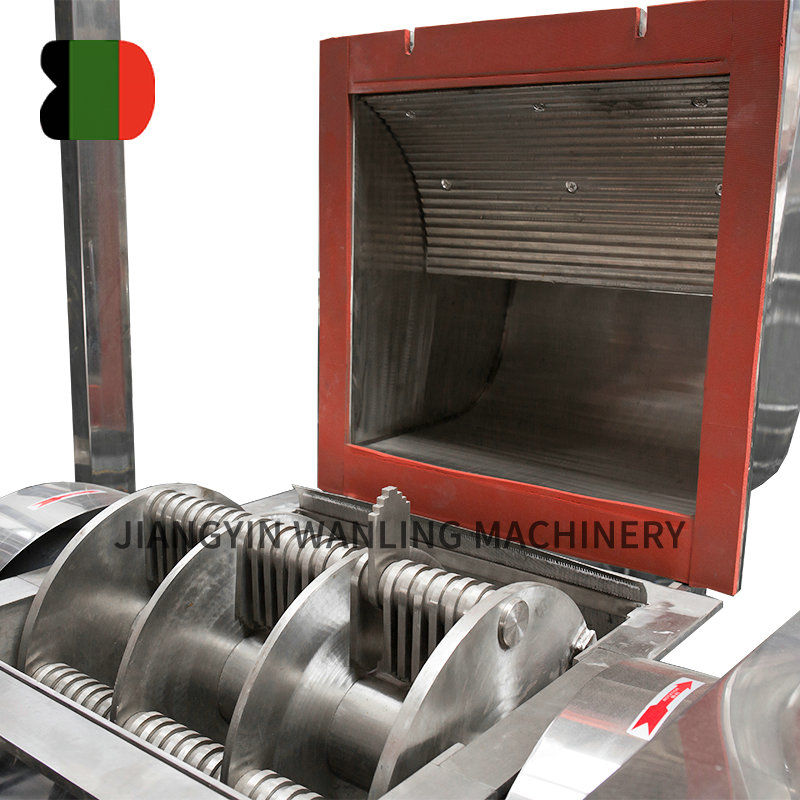
- Rotor: The central rotating element with multiple vanes or pockets that carry material through the valve.
- Housing: The stationary outer body that encloses the rotor and connects to inlet and outlet ducts.
- End Plates and Bearings: Provide structural support and allow smooth rotor rotation.
- Drive System: Typically an electric motor connected through a gearbox to control rotor speed.
- Seals: Reduce air leakage between the rotor and housing to maintain pressure differential.
Working Principle of a Rotary Airlock Valve
The working principle of a rotary airlock valve is based on controlled rotation of the rotor, which allows material to pass from the inlet to the outlet while maintaining a pressure differential between two systems. The operation can be divided into several stages:
Material Intake
Material enters the valve through the inlet hopper and fills the pockets between rotor vanes. The rotor's rotation ensures that the material is carried smoothly without backflow, providing a steady feed to the downstream system.
Airlock Function
The close clearance between the rotor and the housing acts as an airlock, preventing high-pressure air in the pneumatic system from escaping back through the inlet. This is crucial in maintaining system efficiency and preventing material blowback or dust leakage.
Material Discharge
As the rotor rotates, material pockets align with the outlet port. Gravity and rotation force the material to exit the valve continuously. This ensures uniform flow into the downstream pneumatic or mechanical conveying system.
Key Operational Considerations
Proper operation of a rotary airlock valve requires attention to several critical factors:
- Rotor Speed: Determines material throughput and must be calibrated to match system requirements.
- Material Characteristics: Bulk density, particle size, abrasiveness, and moisture content affect flow efficiency and wear.
- Pressure Differential: Proper sealing and rotor clearance prevent air leakage and maintain system pressure.
- Wear and Maintenance: High-abrasion materials may require hardened rotors and regular inspection of seals and bearings.
- Alignment and Installation: Misalignment can cause uneven wear, vibration, or material jamming.
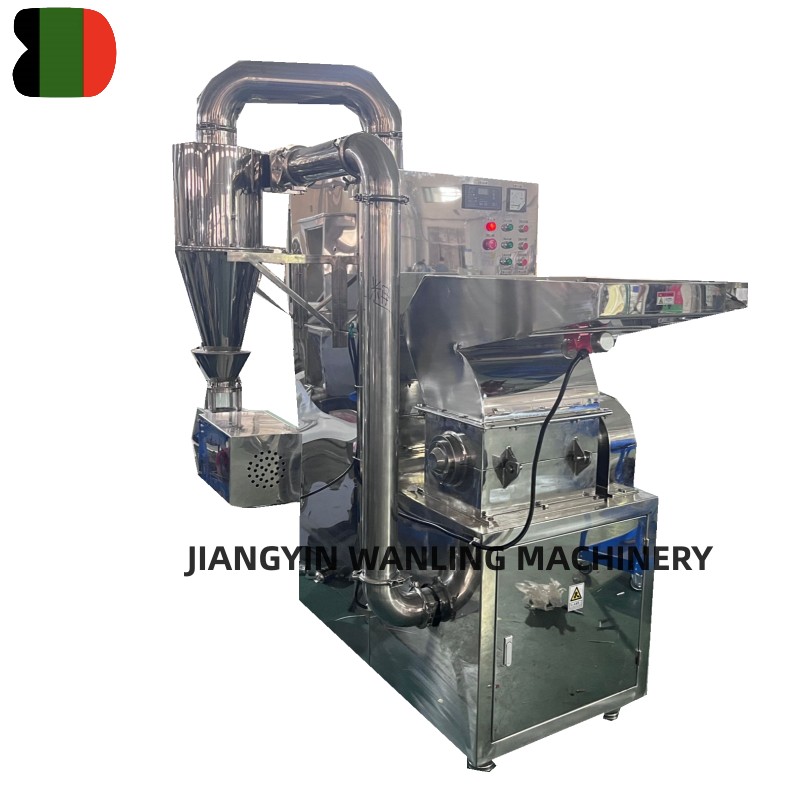
Types of Rotary Airlock Valves
Rotary airlock valves are available in various designs to accommodate different materials and system pressures:
- Standard Rotary Valves: Suitable for general bulk material handling with moderate wear resistance.
- Heavy-Duty Valves: Designed for abrasive or dense materials, often featuring hardened rotors and reinforced housing.
- Explosion-Proof Valves: Used in dust-laden environments where explosion mitigation is critical, incorporating grounding and anti-static measures.
- Sanitary Valves: Used in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries, with smooth surfaces and easy-clean designs to prevent contamination.
Design Considerations
When designing or selecting a rotary airlock valve, several factors must be considered to optimize performance and longevity:
Rotor Pocket Volume
Determines the amount of material conveyed per rotation. Larger pockets increase throughput but may affect sealing efficiency.
Clearance and Sealing
The gap between rotor and housing is critical. Too large causes air leakage, while too small leads to material jamming. Seals or wipers are often installed to maintain efficiency.
Material Compatibility
Valve materials and coatings must resist abrasion, corrosion, or chemical attack from the conveyed material.
Applications Across Industries
Rotary airlock valves are versatile and used in multiple industries:
- Cement Industry: Feeding and discharging powders, maintaining system pressure in pneumatic conveyors.
- Food Processing: Controlled dosing of grains, flour, sugar, and other bulk powders while maintaining hygienic standards.
- Chemical Industry: Handling powdered chemicals, maintaining accurate dosing, and preventing contamination or dust escape.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Precise and sanitary handling of powders in tablet and capsule production lines.
- Plastic and Pellet Handling: Feeding, metering, and isolating pellets in extrusion and molding processes.
Table of Key Specifications
A summary of common rotary airlock valve specifications for industrial selection:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Application Note |
|---|---|---|
| Rotor Diameter | 100–500 mm | Depends on material throughput |
| Rotor Speed | 10–60 RPM | Adjusted to material flow rate |
| Air Pressure Differential | 0.1–0.5 bar | Maintained to prevent air leakage |
| Material Temperature | -20°C to 250°C | Depends on rotor and housing material |
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Regularly inspect rotor and housing for wear, especially with abrasive materials.
- Lubricate bearings according to manufacturer recommendations.
- Check seals and wipers for tight clearance and replace if damaged.
- Ensure drive motors and gearboxes are aligned and functioning smoothly.
- Monitor material flow to detect blockages or uneven feeding.
Conclusion
Rotary airlock valves are indispensable in bulk material handling systems for controlling material flow while maintaining pressure differentials. By understanding their working principle, structure, operational considerations, and industry applications, operators can maximize efficiency, minimize wear, and ensure long-term reliability. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of rotary airlock valves play a critical role in achieving consistent performance across industrial processes.


 Español
Español