Air Tray Dryer Manufacturer
-
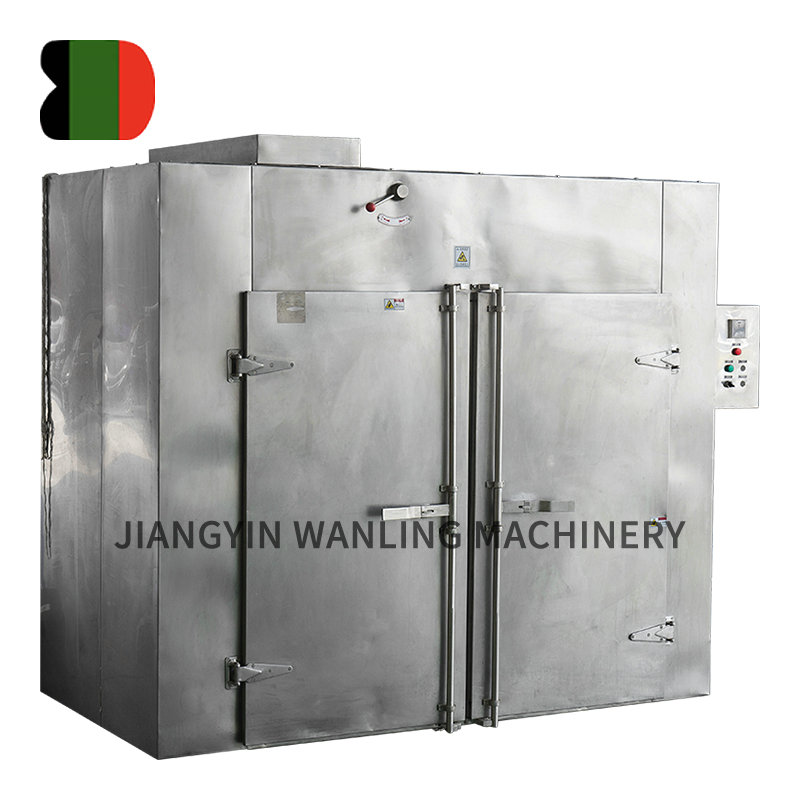


CT Vegetable Hot Air Tray Dryer
CT-C Hot Air Circulation Oven is initiated by our company and reaches the international level after several updates. This machine overcomes ... -
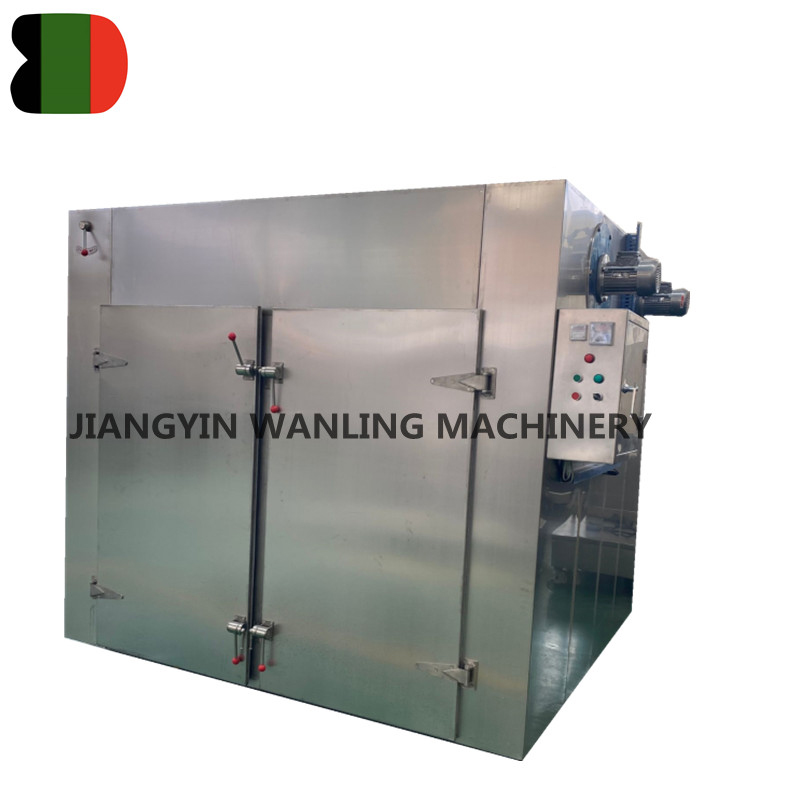


CT Stainless Steel Fruit Tray Dryer
Benefits of using CT Hot Air Tray Dryer for Fruits & Vegetables: Preserves nutrients: Compared to sun drying, hot air drying can better ... -


CT fruit drying machine factory
The fruit drying machine is CT hot air tray dryer, this machine is made of stainless steel, suitable for drying fruits,vegetables and food. ...
The hot air circulation dryer, also known as the hot air circulation oven, is suitable for heating, curing, drying, and dehydration of materials and products in industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food.
The whole machine has low noise and smooth operation. Temperature control, easy installation and maintenance. The material is dried evenly. The heat source can be steam, hot water, electricity, and far-infrared, with a wide range of options.

About Us
Honor
-
 Honor
Honor -
 CE
CE
News
-
Industry News 2026-01-20
Introduction to Fluid Bed Granulators in Powder Processing Fluid bed granulators have become a cruci...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-12
Introduction to Tray Dryers Tray dryers are widely used industrial drying machines designed for dryi...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-06
Introduction to Spice Grinding Machines Grinding machines for spices are essential equipment for bot...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-04
Introduction to Industrial Drying Methods Drying is a critical process in pharmaceutical, chemical, ...
View More
Industry Knowledge Expansion
How efficient is the hot air tray dryer in terms of energy consumption?
The energy efficiency of a hot air tray dryer can vary based on several factors such as its design, size, insulation, airflow management, and the specific drying requirements of the materials being processed.
Efficient hot air tray dryers are engineered to minimize energy consumption while still achieving effective drying results. They typically incorporate features like:
Insulation: High-quality insulation reduces heat loss from the dryer, ensuring that the energy used to heat the air is efficiently utilized for the drying process.
Airflow Optimization: Well-designed airflow systems ensure even distribution of hot air throughout the drying chamber, maximizing heat transfer to the materials and minimizing the need for excessive heating.
Temperature Control: Precise temperature control mechanisms help maintain optimal drying conditions, preventing energy waste from overheating while ensuring thorough drying.
Heat Recovery Systems: Some advanced dryers may include heat recovery systems to capture and reuse waste heat generated during the drying process, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Efficient Heat Sources: Choosing energy-efficient heat sources such as steam, hot water, or electricity, and utilizing them effectively can contribute to overall energy savings.
Size and Load Optimization: Selecting a dryer with an appropriate size for the specific drying load and avoiding overloading or underloading the dryer can optimize energy efficiency.
How does the hot air tray dryer work?
A hot air tray dryer works on the principle of forced convection heating, where hot air is circulated through the drying chamber to remove moisture from materials placed on trays. Here's a step-by-step explanation of how it typically operates:
Loading: The materials to be dried are loaded onto trays arranged within the drying chamber. These trays are usually perforated or have mesh bottoms to allow airflow through the materials.
Heating: The hot air source, which can be steam, hot water, electricity, or infrared radiation, heats the air to the desired temperature. This heated air is then forced into the drying chamber by a fan or blower.
Air Circulation: The fan or blower continuously circulates the hot air throughout the drying chamber. This airflow ensures even distribution of heat and facilitates the removal of moisture from the materials.
Moisture Evaporation: As the hot air passes over the materials, it absorbs moisture from their surface. The moisture evaporates into the air, increasing its humidity.
Exhaust: The humid air, now laden with moisture, is expelled from the drying chamber through an exhaust vent or duct. This helps maintain a consistent drying environment within the chamber.
Condensation: In some cases, the humid air may pass through a condenser or dehumidification system to remove excess moisture before being reheated and recirculated. This helps to prevent the buildup of moisture within the drying chamber and improves drying efficiency.
Drying Completion: The drying process continues until the materials reach the desired moisture content or until a specified drying time is reached. Once drying is complete, the hot air circulation is stopped, and the materials can be removed from the trays.


 Español
Español