Belt Dryer Manufacturer
-
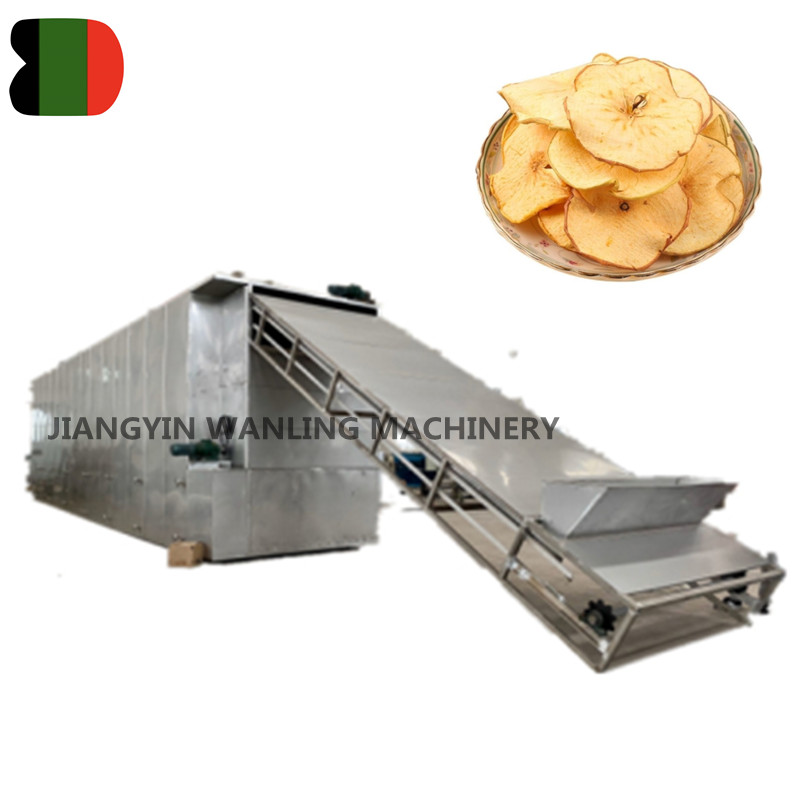

DW high capacity vegetable belt dryer
Mesh Belt Dryer machine is a continuous penetrating flow drying equipment applied for drying pieces strip and particles state materials with... -
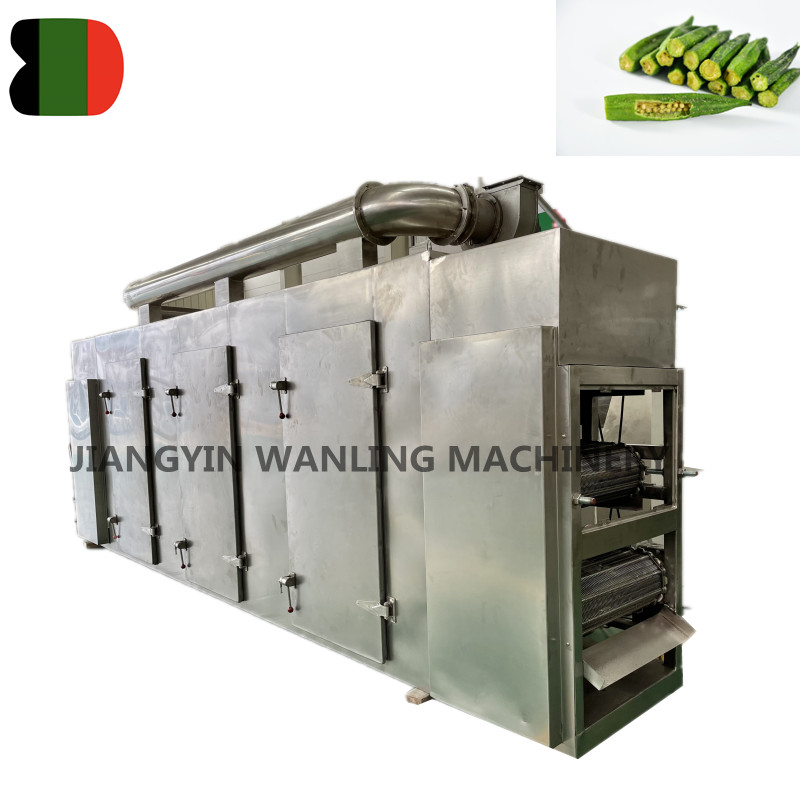

DW Automatic Conveyor Mesh Belt Dryer Machine
The DW automatic conveyor mesh belt dryer machine utilizes a continuous mesh belt conveyor system that gently transports your product throug... -

DW continuous belt dryer machine for vegetables
The belt dryer uses a continuous mesh belt conveyor system that gently transports your product through a multi-sectioned drying chamber. Eac...

About Us
Honor
-
 Honor
Honor -
 CE
CE
News
-
Industry News 2026-01-20
Introduction to Fluid Bed Granulators in Powder Processing Fluid bed granulators have become a cruci...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-12
Introduction to Tray Dryers Tray dryers are widely used industrial drying machines designed for dryi...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-06
Introduction to Spice Grinding Machines Grinding machines for spices are essential equipment for bot...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-04
Introduction to Industrial Drying Methods Drying is a critical process in pharmaceutical, chemical, ...
View More
Industry Knowledge Expansion
Can a belt dryer handle different moisture levels in materials effectively?
Adjustable Parameters: Belt dryers often come with adjustable parameters such as temperature, airflow, and belt speed. These parameters can be tailored to accommodate varying moisture levels in the materials being dried.
Controlled Environment: The drying chamber of a belt dryer provides a controlled environment where temperature and humidity levels can be regulated. This allows for efficient drying of materials with different initial moisture contents.
Uniform Drying: Belt dryers are designed to provide uniform drying across the entire surface area of the material being processed. This ensures that even materials with uneven moisture distribution can be dried effectively without over-drying or under-drying certain areas.
Customization: Depending on the specific requirements of the materials being processed, belt dryers can be customized with different heating and airflow configurations to optimize drying performance for varying moisture levels.
Pre-treatment Options: In some cases, pre-treatment options such as preheating or pre-drying stages can be incorporated into the drying process to prepare materials with higher initial moisture levels for more efficient drying in the belt dryer.
How does the drying uniformity of a belt dryer compare to other drying methods?
Belt Dryers vs. Tray Dryers:
Belt dryers typically offer better drying uniformity compared to tray dryers. In a belt dryer, the material is spread out evenly on a moving conveyor belt, allowing for consistent exposure to heat and airflow throughout the drying process. Tray dryers, on the other hand, may have limited airflow and heating distribution, leading to uneven drying, especially if the trays are not rotated or rearranged during the process.
Belt Dryers vs. Rotary Dryers:
Belt dryers and rotary dryers both have the potential to provide uniform drying, but the effectiveness can vary depending on the specific design and operation. In a belt dryer, the material moves continuously along a horizontal belt, ensuring consistent exposure to heat and airflow. Rotary dryers, which use rotating drums to tumble and agitate the material, can also achieve uniform drying, but may require careful control of rotation speed and internal airflow to prevent uneven drying.
Belt Dryers vs. Fluidized Bed Dryers:
Fluidized bed dryers are known for their excellent drying uniformity, as the material is suspended and fluidized by hot air or gas, ensuring uniform heat and mass transfer. While belt dryers can provide uniform drying, fluidized bed dryers are often preferred for applications where precise control of drying uniformity is critical, such as in pharmaceutical or food processing industries.
Belt Dryers vs. Spray Dryers:
Spray dryers are commonly used for drying liquid materials into powders or granules. While spray dryers can achieve high drying rates and uniformity for certain materials, they may not be suitable for heat-sensitive or sticky substances. Belt dryers offer a gentler drying process, especially for delicate materials, and can provide more consistent drying uniformity across a wide range of materials.


 Español
Español