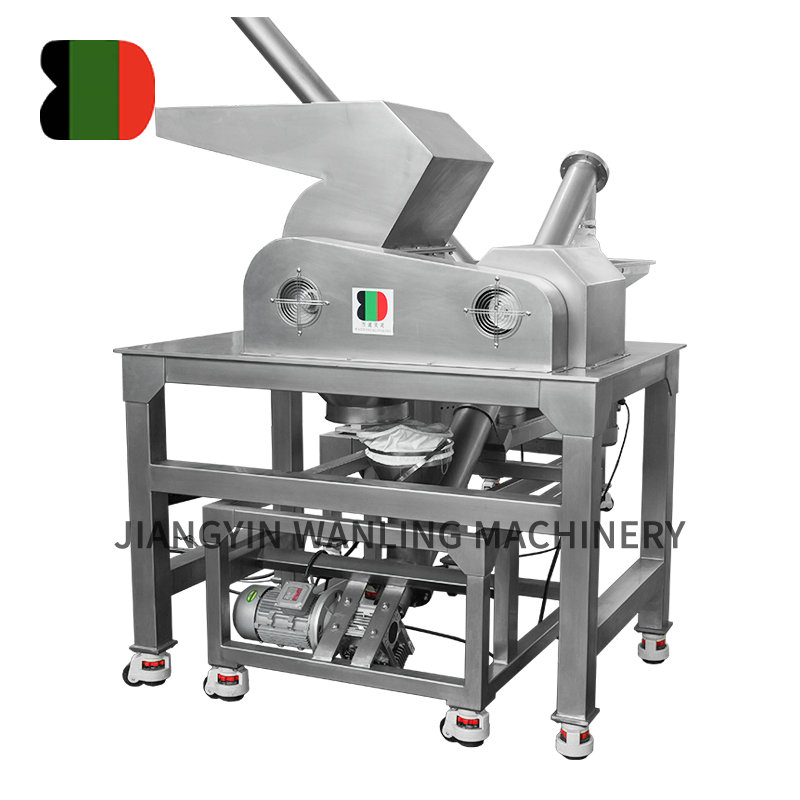
Content
Electric-Powered Tray Dryers
Advantages:
-
Precise and Stable Temperature Control
Electric-powered tray dryers offer the most accurate and consistent control over the temperature, thanks to electric heating elements that can be finely tuned. This is particularly important for industries or applications where precise temperature regulation is crucial. For instance, in food processing or pharmaceuticals, where material properties such as texture or moisture content need to be tightly controlled, electric tray dryers excel by maintaining stable heat distribution throughout the drying process.The ability to fine-tune the temperature without the need for complicated adjustments or manual intervention makes electric dryers a favored option for sensitive applications. This consistent heat delivery means that the product can be dried evenly without the risk of overheating, preserving the material’s quality and integrity.
-
Cleaner and Safer Operation
One of the most compelling advantages of electric dryers is their cleaner operation. Unlike gas dryers, which require combustion, electric dryers don’t produce any exhaust fumes or pollutants such as carbon monoxide or nitrogen oxides. This not only makes them better suited for sterile or controlled environments (such as laboratories, pharmaceutical plants, or food processing facilities), but it also ensures that your drying processes comply with environmental regulations and safety standards.Additionally, electric dryers do not produce combustion-related risks, such as gas leaks or fires, making them inherently safer to use in facilities with stringent safety protocols.
-
Simpler Installation and Maintenance
The installation of electric-powered dryers is typically simpler and more cost-effective than gas-powered dryers, especially in areas where gas infrastructure is not readily available. Electric dryers do not require gas lines, venting systems, or exhaust outlets, which can be difficult and costly to set up. This simplicity also translates to lower maintenance costs in the long term, as there are fewer components that require regular inspection, cleaning, or servicing.In addition, since they run on electricity, they can be installed almost anywhere, provided there is a sufficient power source. For businesses or homes where gas lines are unavailable, electric dryers provide a practical alternative.
-
Quiet and Low Maintenance
Because electric dryers lack the need for combustion, they generally produce less noise during operation. Gas dryers, in contrast, often have loud fans and blowers that handle the exhaust. For facilities or businesses where noise levels are important—such as in office settings or labs—electric dryers offer a quieter and more comfortable operation. -
Better for Smaller Scale Operations
Electric dryers are often the preferred choice for smaller operations or businesses with modest drying needs. They can be scaled down to accommodate small to medium-sized operations, while still providing effective drying performance. For startups or small-scale enterprises, electric dryers represent a low-risk, cost-efficient option.
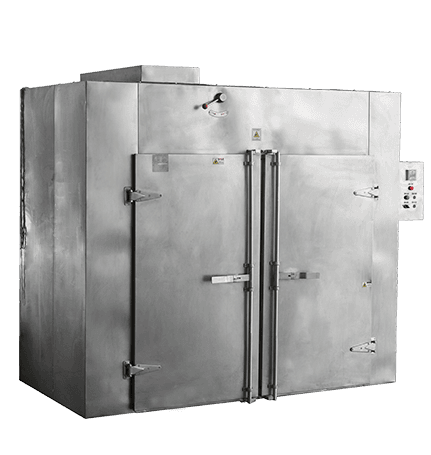

Disadvantages:
-
Higher Operational Costs
One of the most significant drawbacks of electric dryers is their higher operational costs, particularly for large-scale operations. Electricity is generally more expensive than natural gas, and the larger the operation, the more energy-intensive it becomes. Electric dryers require significant electrical energy, which can lead to substantial electricity bills if used continuously.For businesses that need to dry large volumes of material, electric dryers can become less cost-effective over time. This is particularly true in regions where electricity rates are high or where gas is a cheaper alternative.
-
Power Demand and Supply Limitations
Electric dryers require a substantial amount of electrical power, and for large-scale operations, this could mean needing to upgrade the facility’s electrical infrastructure. In places with limited or inconsistent electrical supply, or where power surges are common, this may cause operational disruptions or additional expenses related to power upgrades.The high power demand can also lead to overload issues in facilities where multiple machines or heavy-duty equipment are running simultaneously. This can result in tripped circuits or unreliable performance during peak hours.
-
Limited Heat Output
While electric dryers are excellent for providing consistent heat, they may not be able to produce the same high heat output as gas-powered dryers. Gas dryers tend to have a faster warm-up time and can reach higher temperatures quickly, which makes them more suitable for drying large volumes of material or for industries that require high heat. For instance, industries like mining, ceramics, or chemical processing may require gas dryers for faster, high-volume drying operations. -
Slower Drying in Certain Applications
Electric dryers tend to have slower drying cycles compared to gas dryers, especially when high-temperature drying is necessary. This may make electric dryers less suitable for applications where quick turnaround times are essential or where heat-sensitive materials need to be dried quickly at high temperatures.
Gas-Powered Tray Dryers
Advantages:
-
Lower Operational Costs
In terms of operational efficiency, gas-powered dryers are typically more cost-effective in regions where natural gas is cheaper than electricity. Gas dryers generally offer greater energy efficiency for large-scale applications, as they can produce high heat output at a lower cost.This makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications or industries such as agriculture, food processing, or pharmaceuticals, where large quantities of material need to be dried continuously. Gas dryers offer faster drying cycles due to their powerful heat output, making them more efficient in processing large amounts of material in less time.
-
Higher Heat Output and Faster Drying
Gas-powered dryers excel at generating higher temperatures quickly, which can be crucial for industries that require quick, high-heat drying processes. The ability to reach and maintain high temperatures quickly enables faster drying times, which increases throughput in manufacturing environments.High heat output is particularly advantageous in industries like textile manufacturing, ceramics, and chemical processing, where specific materials require intense and consistent heat to remove moisture effectively.
-
Better for Large-Scale Operations
Gas dryers are typically better suited for large-scale, high-volume operations, where drying needs are continuous and involve substantial quantities of materials. Gas offers an uninterrupted energy source for long-term operations, making them ideal for industrial-scale drying.Businesses that require 24/7 operation often prefer gas-powered dryers for their ability to run efficiently without relying on the electrical grid, providing an energy-intensive drying solution.
-
More Energy-Efficient for Continuous Use
Gas-powered dryers are often more energy-efficient than electric dryers, especially in cases where the dryer is operating continuously or for extended periods. Gas dryers are designed to handle constant high-heat outputs without consuming as much energy as electric alternatives.
Disadvantages:
-
Complex Installation and Maintenance
Gas dryers generally require a more complicated setup compared to electric dryers. They must be connected to a gas supply and require ventilation systems for exhaust gases, which can add to the installation time and cost. Additionally, maintenance of the gas line and burner systems may incur ongoing costs, and if not properly maintained, they may present safety risks. -
Environmental Concerns and Emissions
Gas dryers contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and are less environmentally friendly than electric dryers. They produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants as a result of the combustion process, which can increase a facility’s overall environmental footprint. As regulations around sustainability tighten, companies may face pressure to adopt cleaner technologies. -
Safety Hazards
The use of combustible gas introduces the risk of gas leaks or fire hazards, especially if the dryer is not regularly maintained or properly ventilated. Gas-powered dryers require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure safe operation. Carbon monoxide (CO) buildup and fire risk are significant concerns that require appropriate safety protocols. -
Less Precise Temperature Control
Compared to electric dryers, gas dryers can sometimes struggle with maintaining precise temperature regulation. Temperature fluctuations due to changes in gas supply pressure or inconsistent burner performance can affect drying quality. This is less of a concern in electric dryers, where temperature is consistently monitored and regulated with high precision.
Conclusion
The choice between electric and gas-powered tray dryers will depend heavily on your specific drying needs, budget, and environmental considerations. Electric dryers offer cleaner, safer operation, with precise temperature control and are well-suited for smaller-scale or sensitive drying processes. However, they can be less efficient for high-volume applications due to higher operating costs and slower drying times.
On the other hand, gas dryers are ideal for large-scale operations, offering faster drying, higher heat output, and lower operational costs. However, they come with the drawbacks of higher installation complexity, potential environmental concerns, and safety risks associated with combustion.


 Español
Español