A double cone blender has distinct advantages and limitations when compared to ribbon blenders and V-blenders in industrial applications. The differences mainly involve mixing efficiency, material handling, and suitability for specific powders or granules. Here’s a detailed comparison:
Content
1. Mixing Principle and Efficiency
- Double Cone Blender: Uses a rotating double-cone vessel that continuously tumbles the material. This produces a gentle, three-dimensional mixing action ideal for free-flowing, dry powders and granules. It achieves uniform mixing with minimal shear, preserving the integrity of fragile or shear-sensitive materials.
- Ribbon Blender: Features a horizontal U-shaped trough with inner and outer helical ribbons that push materials in opposite directions. This creates high-shear mixing, which is faster and more aggressive, making it suitable for dense, sticky, or cohesive powders, but less ideal for fragile particles.
- V-Blender: Consists of two cylindrical sections joined in a V-shape that rotates to tumble powders. The V-blender is similar to a double cone in its low-shear, gentle mixing, but the geometry can make it slightly less efficient for very small batches or highly free-flowing materials compared to the double cone.
2. Material Suitability
- Double Cone Blender: Best for fragile, free-flowing powders, pharmaceutical granules, or chemicals that should not be broken down by shear. It is less effective for sticky, moist, or heavy materials.
- Ribbon Blender: Ideal for sticky, damp, or heavy powders due to its high-shear ribbons, which prevent material from clumping. However, excessive shear can degrade sensitive materials.
- V-Blender: Suitable for dry powders and small-to-medium batches; works well when gentle mixing is required, similar to the double cone but may require longer mixing times for uniformity in large batches.
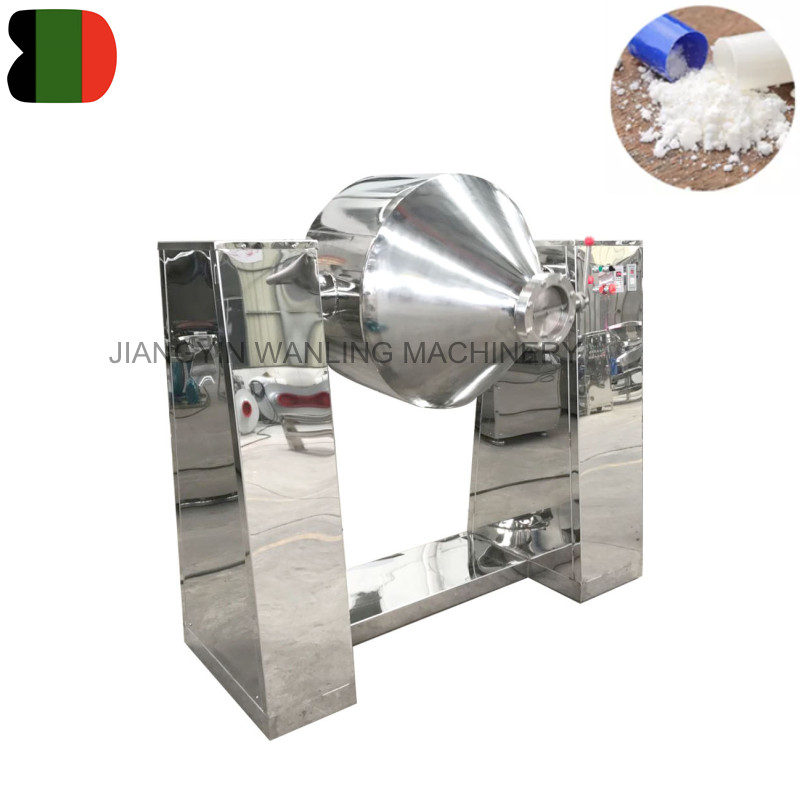

3. Batch Size and Scalability
- Double Cone Blender: Offers excellent scalability for medium to large batch production, with relatively uniform mixing throughout the vessel. The design allows easy scaling without significant changes to mixing quality.
- Ribbon Blender: Commonly used for large industrial batches, with faster mixing times due to the active movement of the ribbons. It may require more power for very large volumes.
- V-Blender: Generally suitable for small to medium batches, though industrial-sized V-blenders exist. Scaling may require longer mixing times for larger batches.
4. Shear and Particle Integrity
- Double Cone Blender: Very low-shear, preserving particle size and structure, making it suitable for pharmaceuticals, food powders, and fragile chemicals.
- Ribbon Blender: High-shear action can break down soft or delicate particles, so it’s less suitable for fragile materials.
- V-Blender: Low-shear like double cone, but may be slightly less uniform for certain powders due to dead zones in the V junction.
5. Cleaning and Maintenance
- Double Cone Blender: Generally easier to clean due to smooth interior surfaces, fewer moving parts, and minimal contact points. Ideal for industries requiring frequent batch changes.
- Ribbon Blender: More complex cleaning due to inner and outer ribbon layers and tight corners. Cross-contamination risk is higher.
- V-Blender: Easy to clean, though the V junction can trap some fine powders if not properly designed.
6. Summary of Comparison
| Feature | Double Cone Blender | Ribbon Blender | V-Blender |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing Action | Gentle, low-shear, 3D tumbling | High-shear, directional | Gentle, low-shear, tumbling |
| Best For | Fragile, free-flowing powders | Sticky, damp, dense powders | Dry powders, small-medium batches |
| Batch Size | Medium to large | Medium to large | Small to medium (industrial versions exist) |
| Mixing Time | Moderate | Fast | Longer than ribbon, similar to double cone |
| Particle Integrity | Excellent | May degrade soft particles | Excellent |
| Cleaning | Easy | Difficult | Easy |
Conclusion:
The double cone blender is ideal when gentle, uniform mixing is required, especially for fragile or shear-sensitive powders. Ribbon blenders excel in high-shear applications for sticky or heavy powders, while V-blenders are similar to double cones but may have slightly lower mixing efficiency for certain materials. The choice depends on the material properties, batch size, and required shear conditions.


 Español
Español