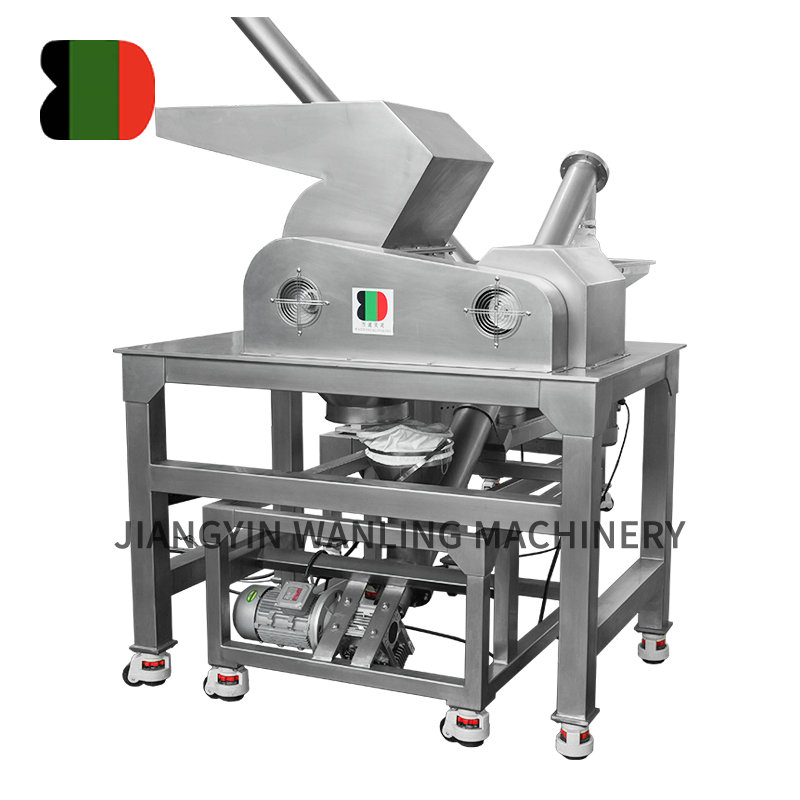
Ribbon blenders are among the most versatile pieces of industrial mixing equipment. Designed to efficiently combine powders, granules, and other bulk solids, they are widely used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, plastics, and construction materials. The choice of materials for building ribbon blenders is not only a matter of mechanical strength but also one of hygiene, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with the blended substances.
Below is an overview of the most commonly used materials in ribbon blender construction and the reasons they are chosen.
Content
1. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is by far the most widely used material for ribbon blenders, especially in industries where sanitation and corrosion resistance are priorities.
-
Grades Used:
- 304 stainless steel: Often used in food, cosmetics, and general-purpose applications where resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning are essential.
- 316 stainless steel: Preferred in pharmaceutical, chemical, and highly corrosive environments because of its superior resistance to chlorides and harsh chemicals.
-
Advantages:
- Non-reactive and hygienic surface
- Easy to clean and maintain
- Long service life, even in aggressive environments
- Meets regulatory standards for food and pharmaceutical use
Because of these properties, stainless steel is the top choice for industries where contamination risks must be minimized.
2. Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is another material often used in ribbon blender construction, particularly for blending applications that do not involve food or sensitive chemicals.
-
Characteristics:
- Strong and cost-effective
- Suitable for construction materials, minerals, and bulk industrial products
- Can be coated or painted to resist corrosion
-
Limitations:
- Susceptible to rust and corrosion without protective coatings
- Not suitable for food, pharmaceuticals, or moisture-sensitive applications
Carbon steel ribbon blenders are commonly used in industries where blending is required for dry bulk materials such as cement, fertilizers, or pigments, and where cost efficiency is a priority.

3. Mild Steel with Special Coatings
In certain applications, mild steel ribbon blenders are manufactured with specialized coatings or linings to improve performance.
-
Options Include:
- Epoxy coatings to provide chemical resistance
- Non-stick coatings for handling sticky or adhesive materials
- Abrasion-resistant linings for blending minerals or abrasive powders
These enhancements extend the life of the equipment and improve blending efficiency in demanding environments.
4. Alloy Steels and Specialty Metals
For heavy-duty or highly specialized applications, manufacturers may use alloy steels or specialty metals.
-
Applications:
- Abrasion-resistant steels for blending highly abrasive powders or minerals
- Nickel-based alloys for high-temperature or extremely corrosive environments
Although more costly, these materials are selected when process requirements exceed the performance of standard stainless or carbon steels.
5. Ancillary Materials
Beyond the main construction, ribbon blenders also include components made from other materials:
- Seals and gaskets: Often made from food-grade rubber, PTFE (Teflon), or elastomers to prevent leakage and contamination.
- Bearings and shafts: Typically manufactured from hardened steel or stainless steel to withstand mechanical stress.
- Drive components and couplings: Designed from durable alloys to manage torque and operational loads.
These supporting materials are critical to ensuring the overall reliability and safety of the blender.
Conclusion
The selection of materials for ribbon blender construction depends largely on the industry, the type of materials being blended, and the regulatory requirements.
- Stainless steel (304 or 316) dominates in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries due to its cleanliness and corrosion resistance.
- Carbon steel and mild steel with coatings are favored in construction materials, plastics, and minerals processing where cost efficiency is important.
- Specialty alloys are reserved for highly abrasive, corrosive, or extreme operating conditions.
By carefully matching the construction material to the application, manufacturers ensure that ribbon blenders deliver both performance and longevity in diverse industrial environments.


 Español
Español