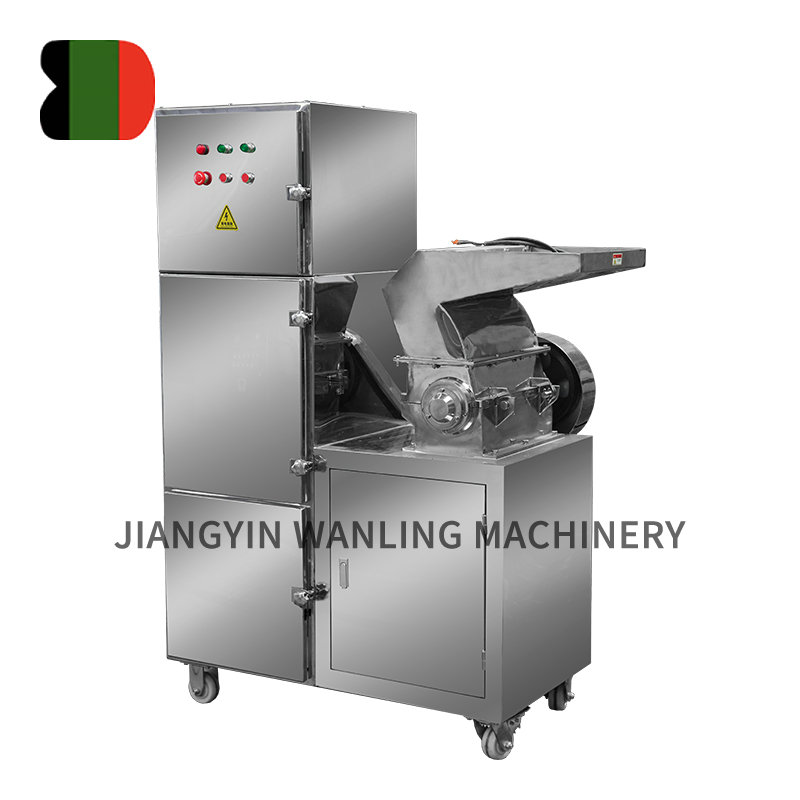
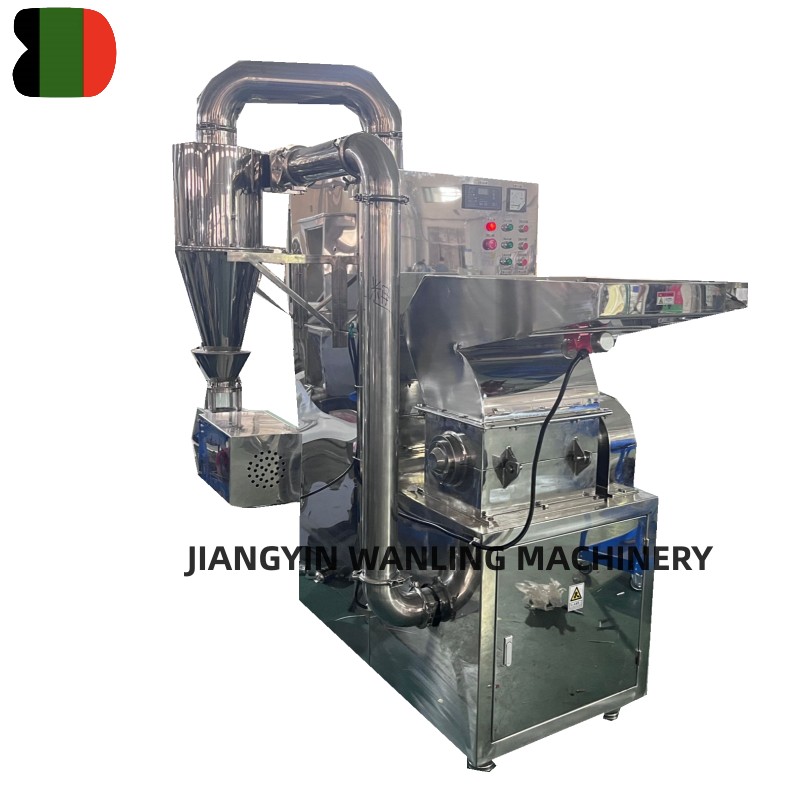
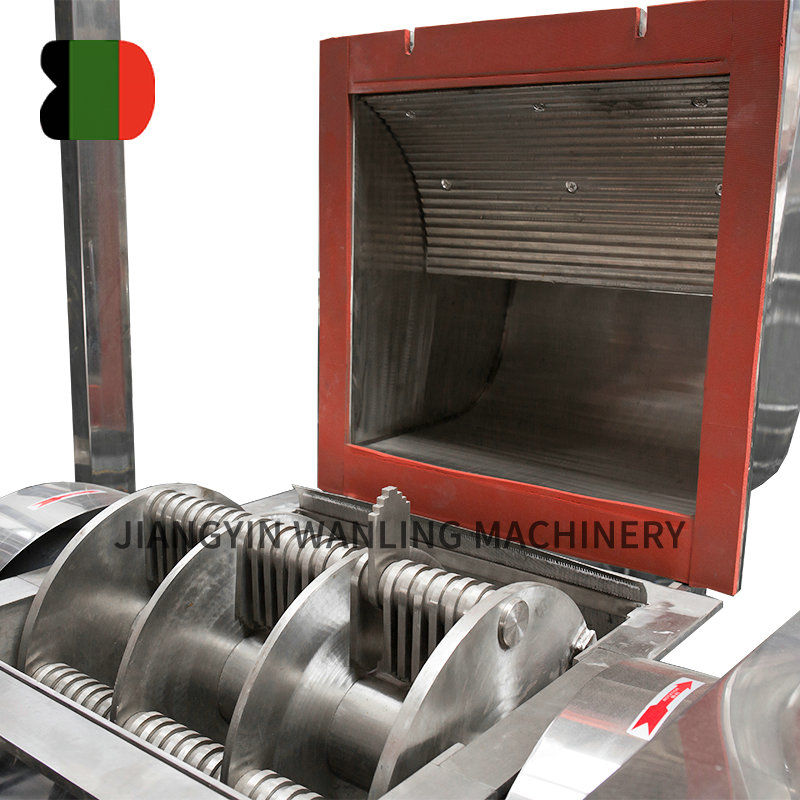
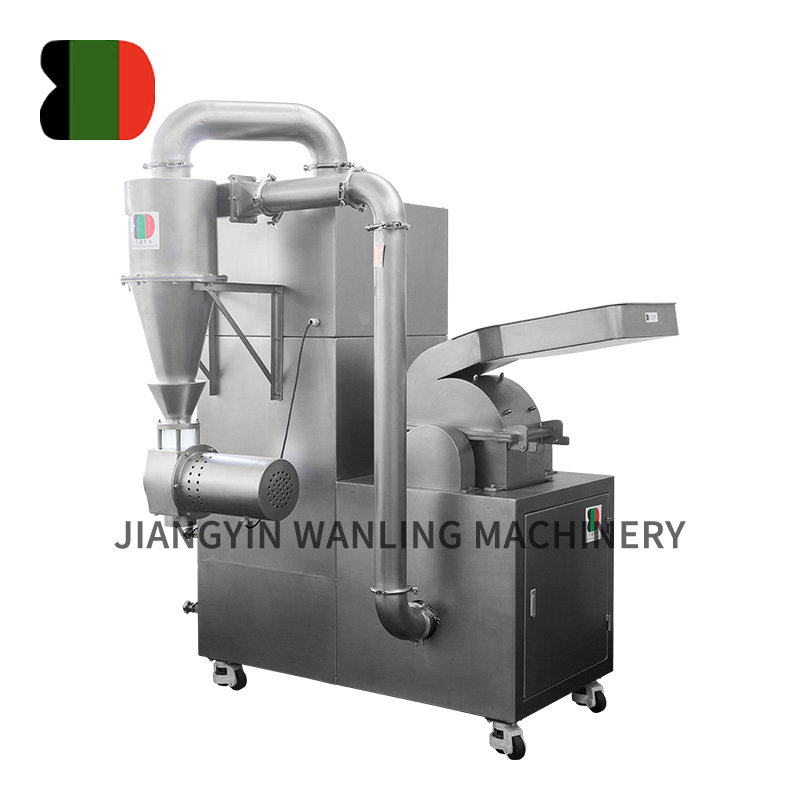
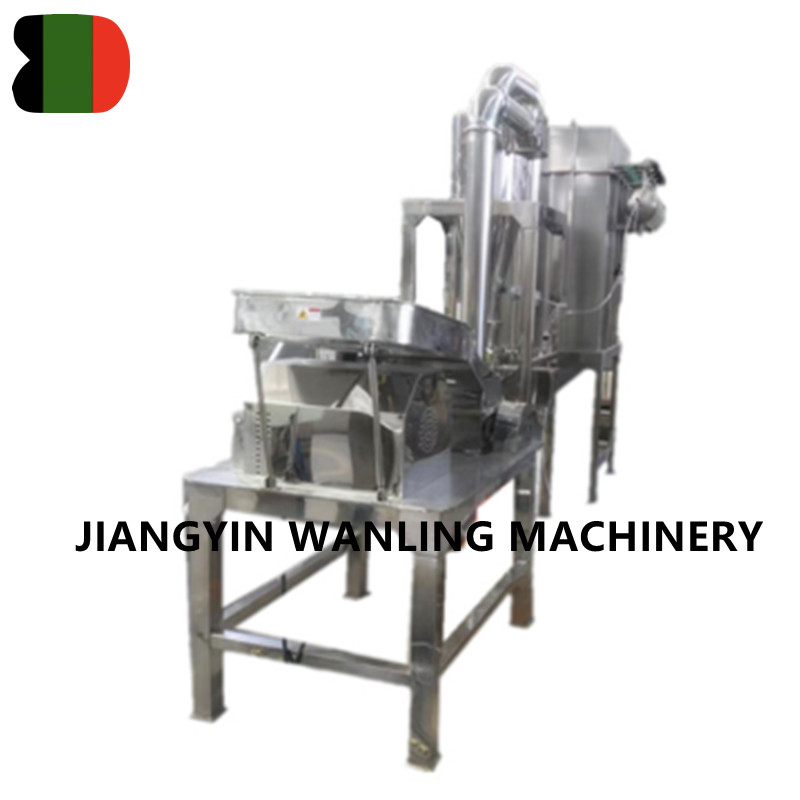
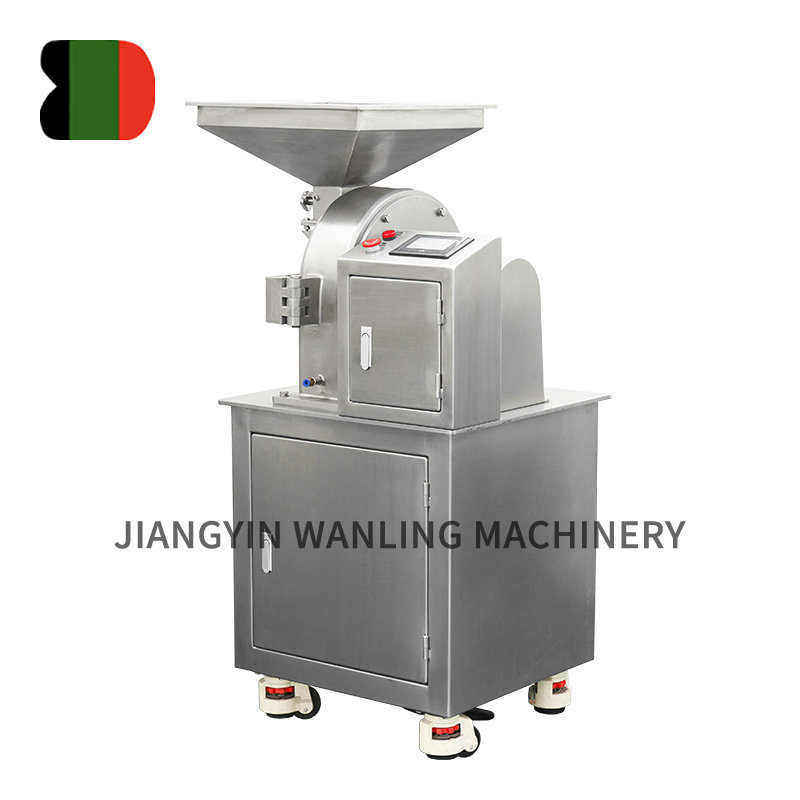
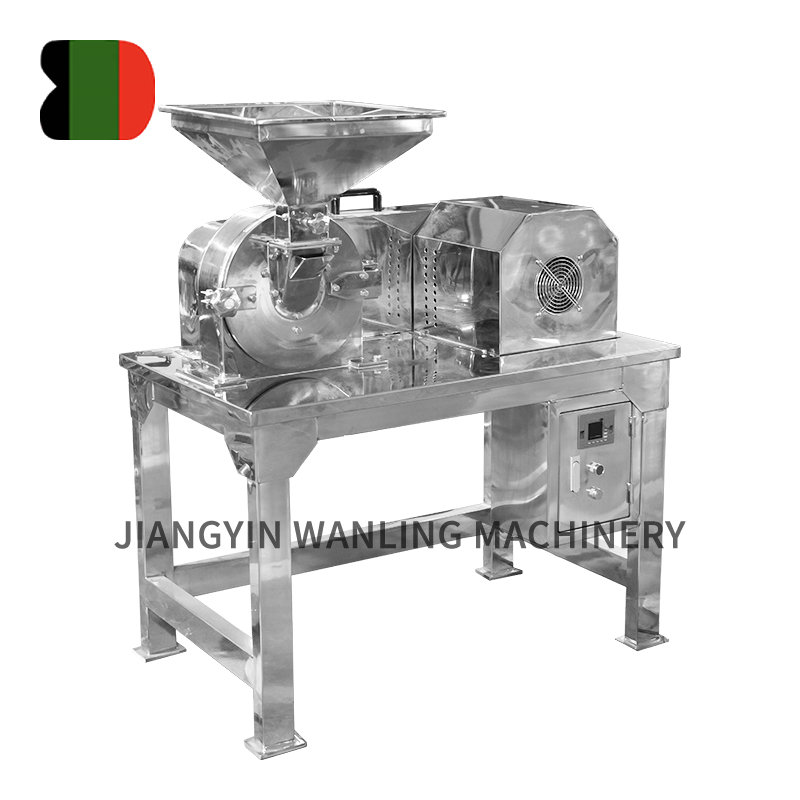
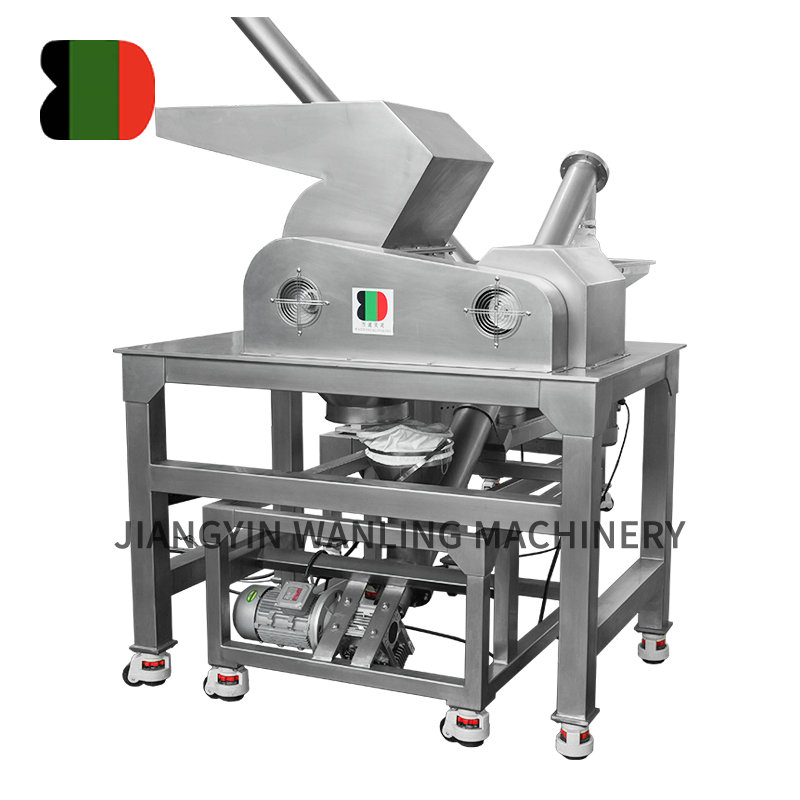
Across industries ranging from agriculture to recycling and pharmaceutical production, hammer mills have established themselves as indispensable workhorses for particle size reduction. These robust machines continue to evolve, offering increasingly efficient solutions for processing everything from grains to electronic waste.
Content
Understanding Hammer Mill Technology
At their core, hammer mills operate on a simple but effective principle:
-
Feeding Mechanism - Material enters through a controlled feed system
-
Impact Zone - Rotating hammers (typically ranging from 1,000 to 3,600 RPM) strike the material
-
Size Classification - Particles pass through screens of specified apertures
-
Discharge - Sized material exits the milling chamber
Modern hammer mills incorporate advanced features that significantly enhance their capabilities:
-
Variable Frequency Drives allowing real-time speed adjustment
-
Air Assist Systems improving throughput of light materials
-
Heavy-Duty Bearings rated for continuous operation
-
Quick-Change Screen mechanisms minimizing downtime
Key Applications Across Industries
Agricultural Processing
-
Grain milling (corn, wheat, soybeans)
-
Biomass preparation for biofuels
-
Animal feed production
Industrial Manufacturing
-
Powder production for chemicals
-
Size reduction of plastic pellets
-
Wood fiber processing for composite materials
Recycling Operations
-
Electronic waste processing
-
Automobile shredder residue refinement
-
Paper and cardboard recycling
Pharmaceutical Production
-
Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) milling
-
Excipient processing
-
Herbal medicine preparation
Technical Advancements Driving Efficiency
The latest generation of hammer mills incorporates several technological improvements:
Material Science Innovations
-
Tungsten carbide hammer tips extending wear life by 300%
-
Composite screen materials resisting abrasion
-
Ceramic-coated interiors for corrosive applications
Operational Enhancements
-
Vibration monitoring systems predicting maintenance needs
-
Automated screen tensioning systems
-
Integrated temperature sensors preventing thermal damage
Safety Features
-
Explosion-proof designs for combustible dusts
-
Magnetic separators protecting downstream equipment
-
Zero-motion start interlocks
Selecting the Right Hammer Mill
Critical factors to consider when specifying a hammer mill:
Material Characteristics
-
Bulk density
-
Moisture content
-
Abrasiveness
-
Heat sensitivity
Performance Requirements
-
Desired particle size distribution
-
Throughput capacity
-
Energy efficiency targets
Operational Parameters
-
Continuous vs. batch operation
-
Cleanability requirements
-
Noise level restrictions
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The global hammer mill market is projected to grow steadily, driven by:
Sustainability Initiatives
-
Increased recycling mandates worldwide
-
Growing biomass energy sector
-
Circular economy adoption in manufacturing
Technological Integration
-
IoT-enabled mills providing real-time analytics
-
AI-driven optimization of milling parameters
-
Hybrid systems combining multiple size reduction methods
Emerging Applications
-
Cannabis processing for legal markets
-
Specialty food ingredient production
-
Advanced material recycling for battery components
Maintenance and Optimization Practices
To maximize hammer mill performance and longevity:
-
Preventive Maintenance
-
Regular bearing lubrication
-
Screen integrity checks
-
Hammer tip inspection
-
Operational Best Practices
-
Proper feed rate control
-
Moisture content management
-
Correct screen selection
-
Performance Monitoring
-
Particle size analysis
-
Energy consumption tracking
-
Throughput measurement
Conclusion
Today's hammer mills represent a perfect marriage of proven mechanical principles and cutting-edge technological enhancements. As material processing requirements become more sophisticated across industries, hammer mill manufacturers continue to innovate, offering solutions that deliver precise particle size control with unprecedented efficiency.
From small laboratory models processing grams per hour to industrial behemoths handling tons of material, the modern hammer mill remains an essential tool for countless operations. Their versatility, reliability, and continuous technological improvement ensure they will remain at the heart of size reduction processes for decades to come.


 Español
Español