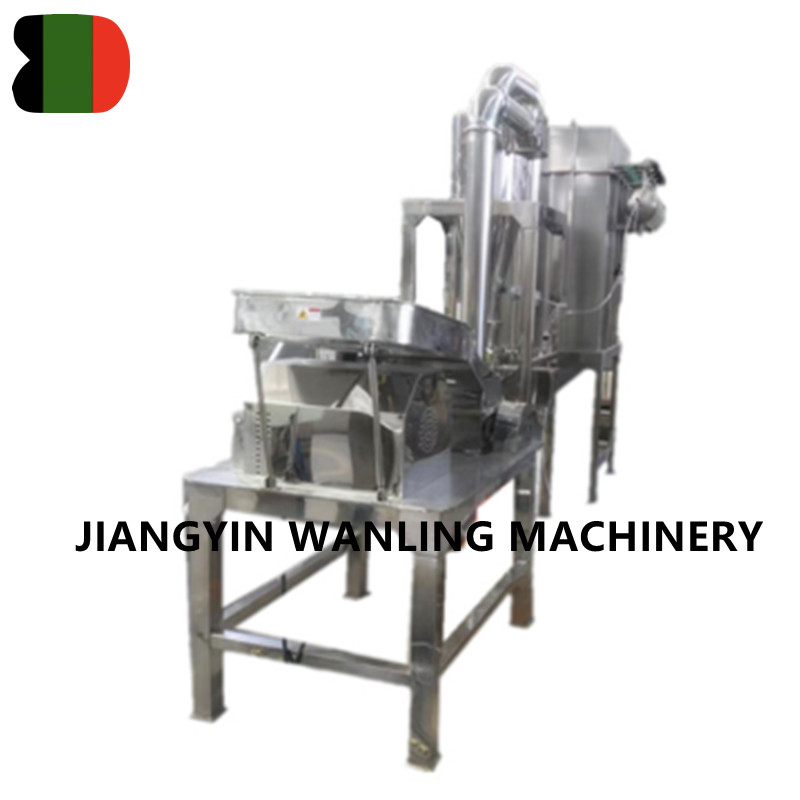
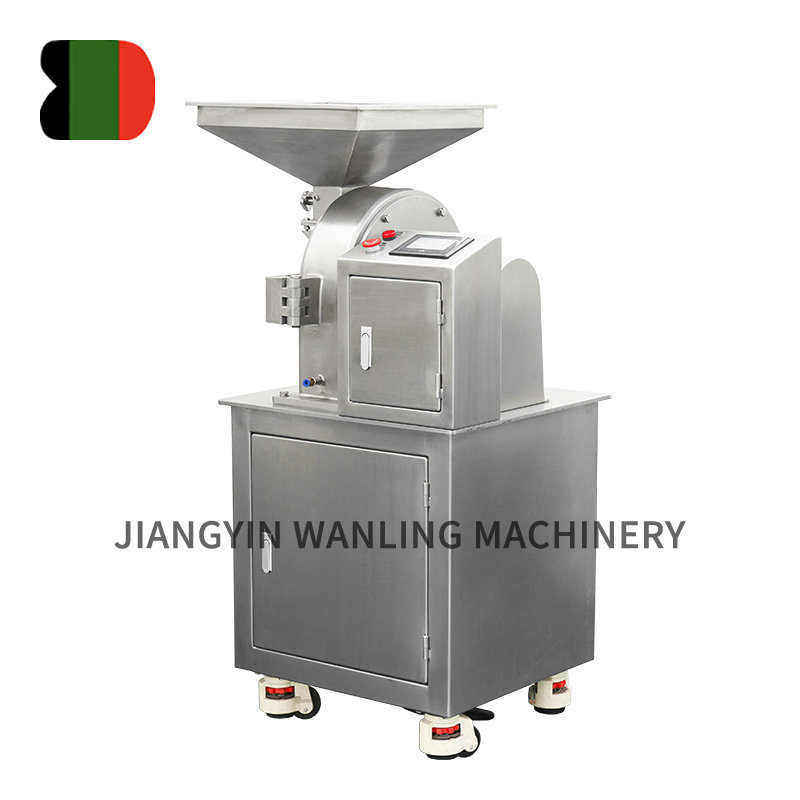
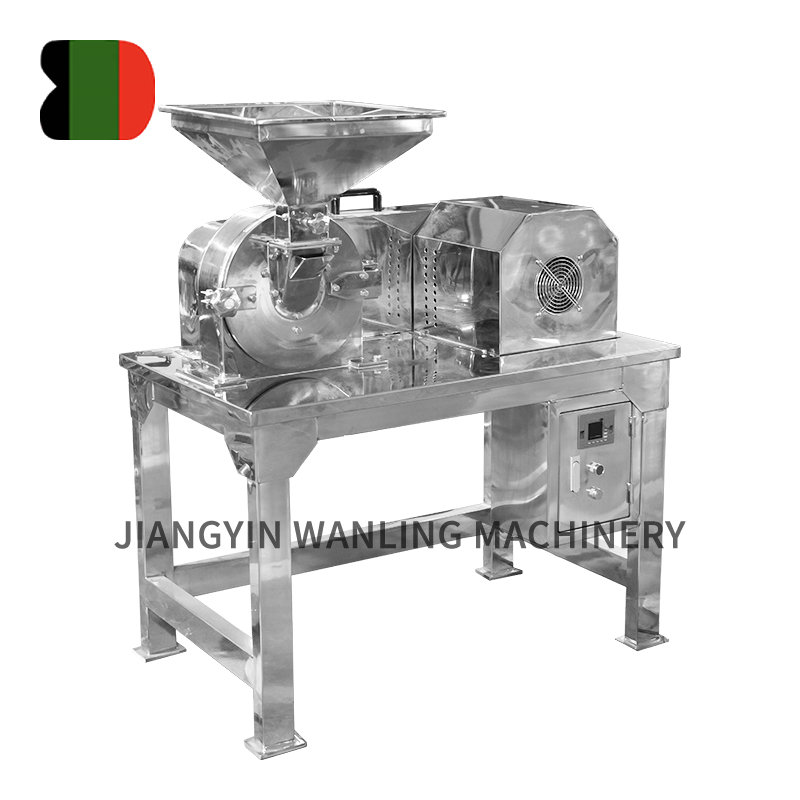
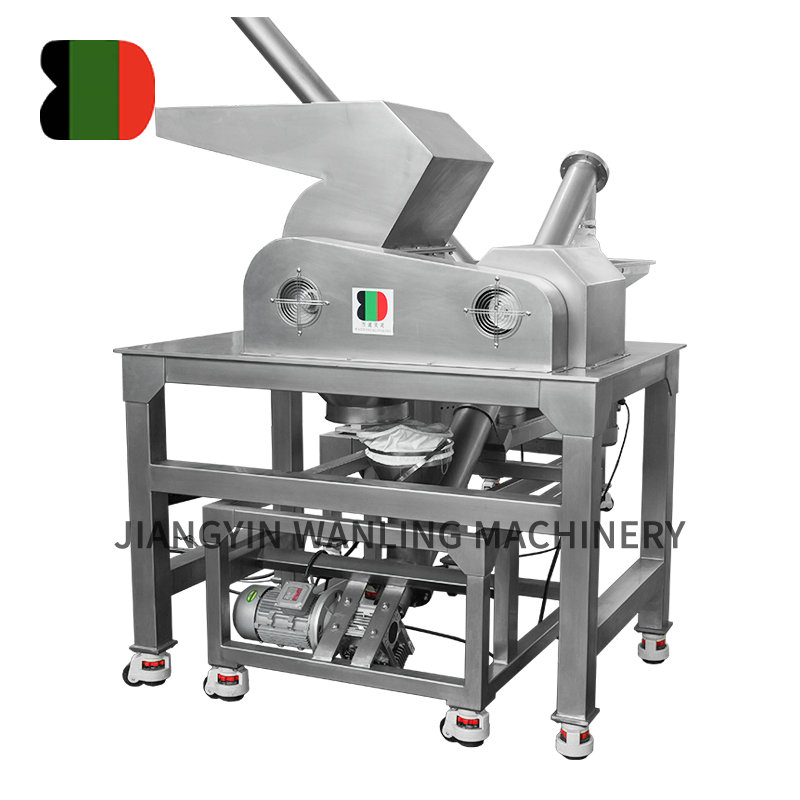
Air classifier mills (ACMs) are highly efficient grinding and classification systems widely used across industries for precise particle size reduction and separation. Combining impact milling and air classification in a single unit, these mills offer superior control over particle size distribution (PSD), making them indispensable in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, minerals, and food processing. This article explores the working principles, key components, industrial applications, and recent advancements in air classifier mill technology.
Content
Working Principle of Air Classifier Mills
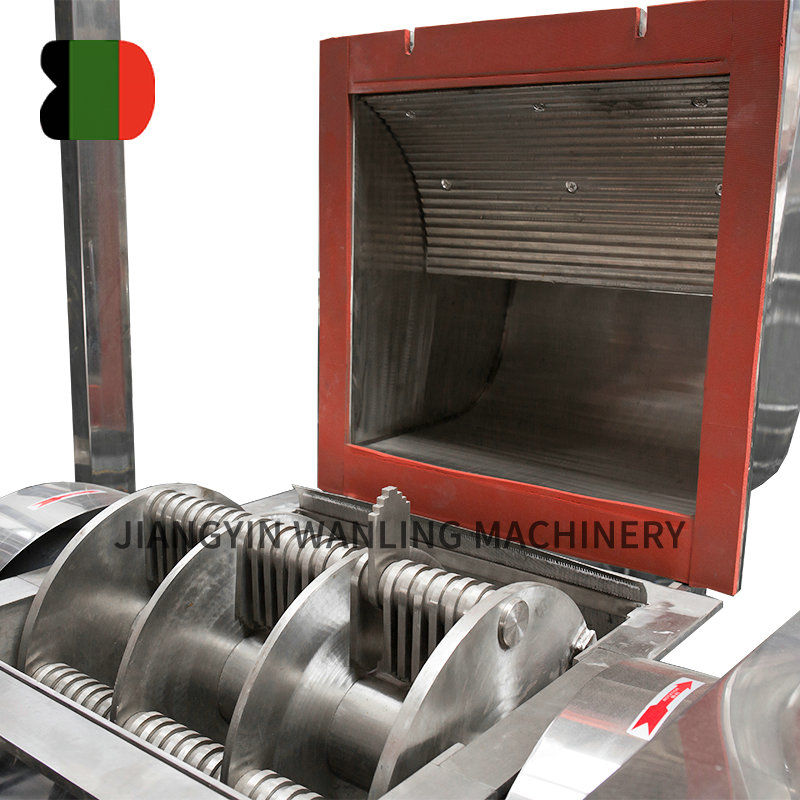
The air classifier mill operates on a dual mechanism of size reduction (via mechanical impact) and dynamic classification (via centrifugal and aerodynamic forces). The process involves:
-
Feed Introduction – Material is fed into the grinding chamber, where rotating hammers or pins deliver high-impact forces.
-
Grinding & Dispersion – The intense mechanical action breaks down particles, while an integrated air stream fluidizes and transports the material.
-
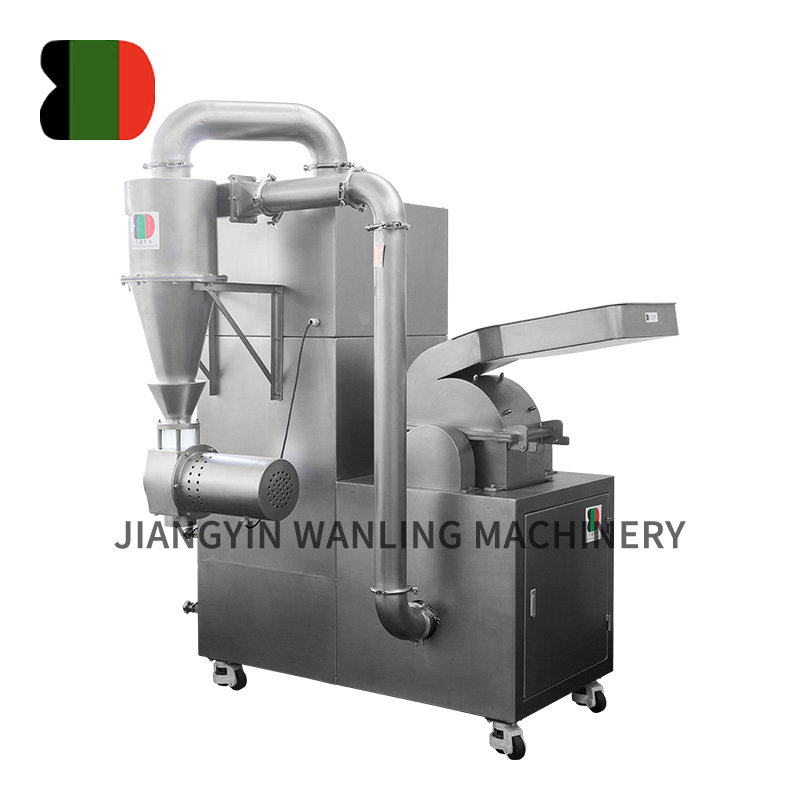
Classification – The ground particles enter an air classifier wheel, where centrifugal force separates fines from coarse particles. Fine particles exit with the air stream, while coarse particles are recirculated for further grinding.
-
Collection – The classified product is collected in a cyclone or bag filter, ensuring minimal fines loss and high efficiency.
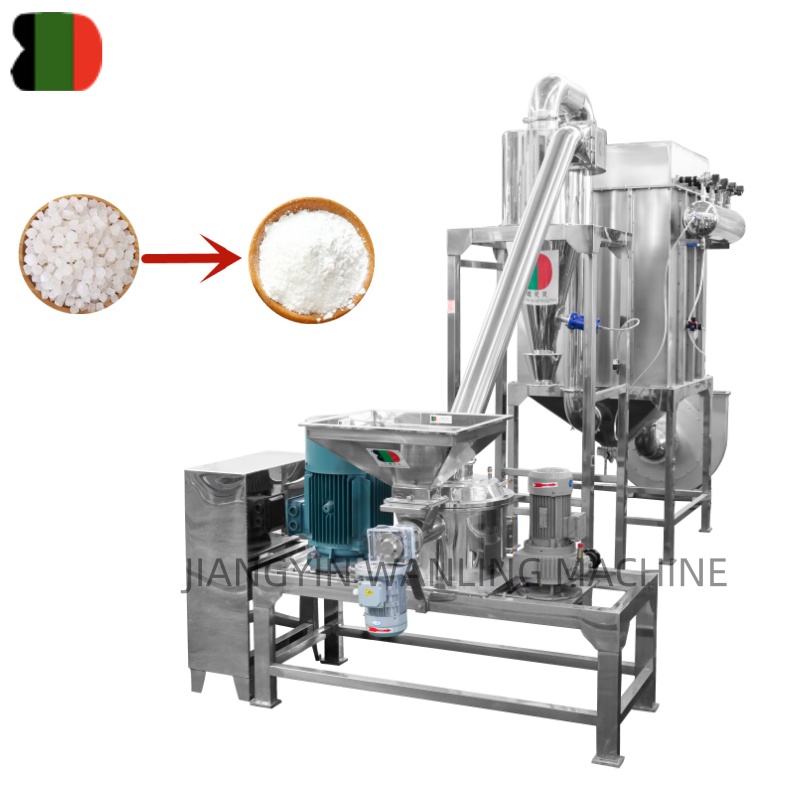

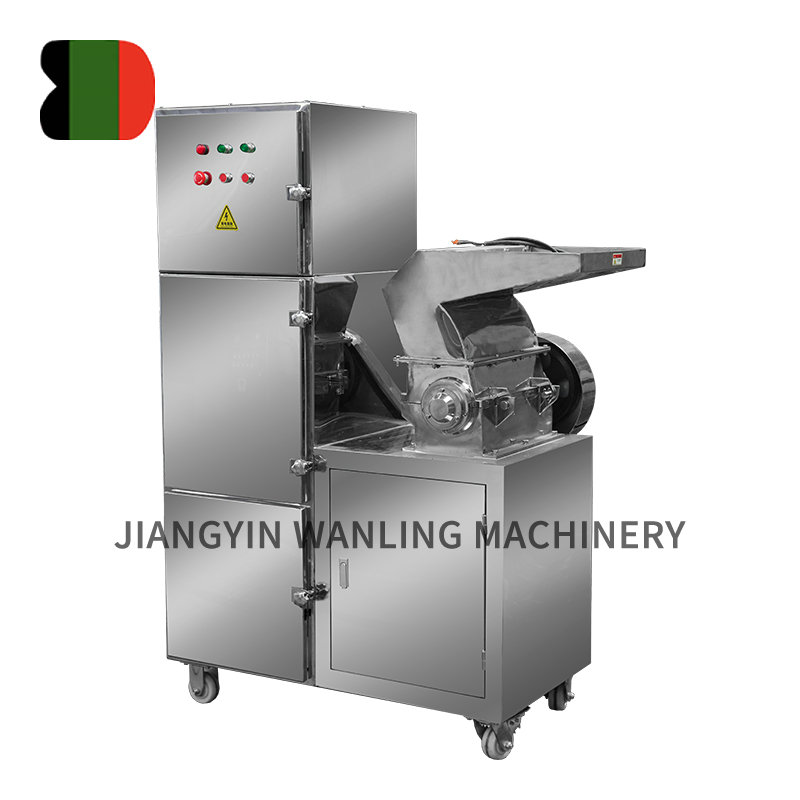
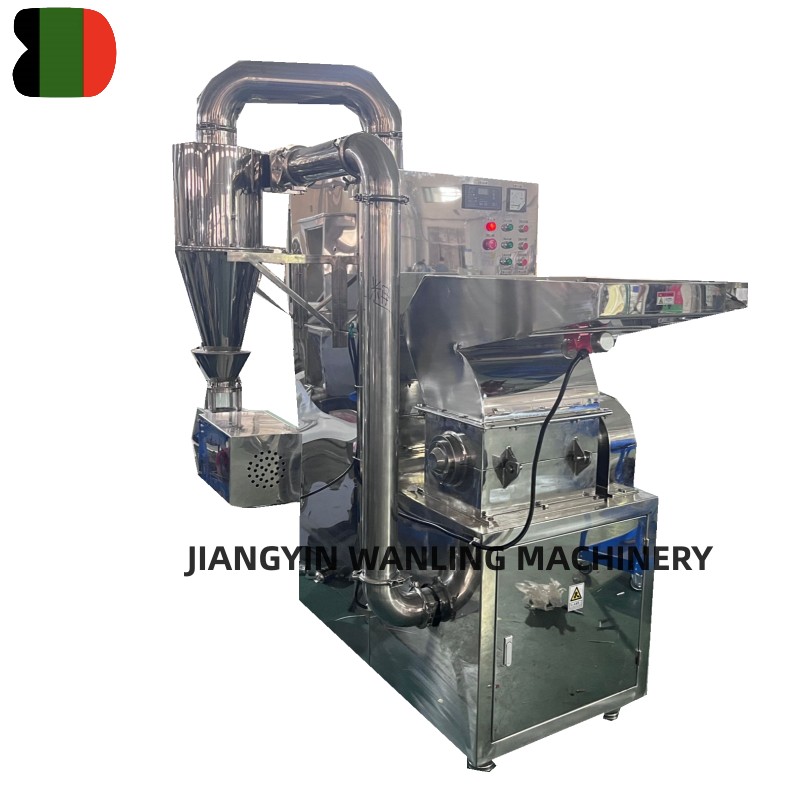
Key Components of an Air Classifier Mill
-
Grinding Chamber – Equipped with a rotor and impact elements (hammers, pins, or blades) for particle size reduction.
-
Classifier Wheel – Adjustable speed controls cut-point precision (typically 5–200 microns).
-
Air System – Provides airflow for material transport and classification.
-
Drive System – High-speed motor for rotor and classifier operation.
-
Product Collection – Cyclones, bag filters, or electrostatic precipitators for efficient fines recovery.
Industrial Applications
Air classifier mills are versatile and used in:
-
Pharmaceuticals – Micronization of APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) for enhanced bioavailability.
-
Chemicals – Fine grinding of pigments, dyes, and specialty chemicals.
-
Food & Nutraceuticals – Production of powdered spices, flavors, and protein isolates.
-
Minerals & Ceramics – Processing of talc, calcium carbonate, and silica.
-
Recycling – Size reduction of plastics and composite materials.
Technological Advancements
-
AI-Based Process Optimization – Smart control systems adjust rotor speed and airflow in real-time for optimal PSD.
-
Energy-Efficient Designs – Improved airflow dynamics reduce power consumption.
-
Hygienic & Containment Models – FDA-compliant designs for pharmaceuticals and food-grade applications.
-
Nanoparticle Production – Ultra-fine classifiers enable sub-micron grinding.
Conclusion
Air classifier mills represent a critical advancement in powder processing, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and versatility. With ongoing innovations in automation and energy efficiency, ACMs continue to revolutionize industries requiring ultra-fine grinding and classification. Future developments may focus on hybrid milling-classification systems and sustainable processing solutions.
By understanding their operational mechanics and applications, industries can leverage air classifier mills to achieve superior product quality and process efficiency.


 Español
Español