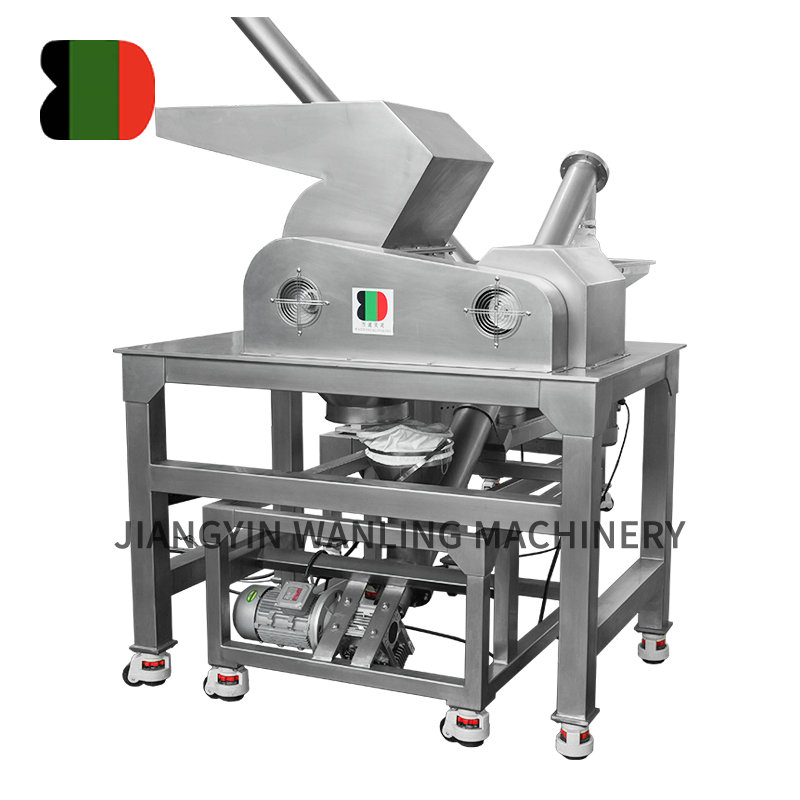
A ribbon blender is a widely used industrial mixing machine designed for the gentle and efficient blending of bulk solids, powders, pastes, and granules. Its signature feature—intertwined inner and outer helical ribbons—facilitates thorough axial and radial mixing, making it suitable for a broad spectrum of materials across various industries. The versatility of the ribbon blender lies in its ability to handle dry, moist, and even mildly viscous substances.
Below is a breakdown of the most commonly processed materials and ingredients in ribbon blenders, categorized by application area:
1. Food Industry
The food industry relies heavily on ribbon blenders for their ability to achieve consistent blends without damaging sensitive ingredients.
Common materials include:
Powdered ingredients: flour, sugar, salt, baking soda, milk powder, cocoa powder
Seasoning blends: spice mixtures, curry powder, herbal powders
Bakery premixes: cake mix, pancake mix, biscuit dough base
Dry beverage mixes: coffee blends, tea powders, instant drink powders
Nutritional products: protein powder, vitamin blends, dietary supplements
Ribbon blenders used in food applications are typically constructed with food-grade stainless steel and may include sanitary features such as quick-clean access doors and polished surfaces.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceutical production, the ribbon blender is valued for its precision in homogenizing fine powders used in tablet and capsule formulations.
Typical materials include:
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
Excipients: lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, starches
Nutraceutical powders: herbal extracts, protein complexes, mineral blends
Coating agents: magnesium stearate, talc, silicon dioxide
Blenders for pharmaceutical use often meet cGMP standards and include features such as dust-tight seals, validation-ready controls, and fully jacketed mixing troughs for temperature control.
3. Chemical Industry
Ribbon blenders handle a wide range of chemical powders and granules where precise blending and safe material handling are essential.
Commonly blended chemicals include:
Pigments and colorants
Fertilizers and soil additives
Detergent powders
Dry catalysts
Plastic and polymer additives
Cleaning agents and desiccants
In these applications, corrosion resistance and explosion-proof designs may be required, depending on the chemical composition and reactivity of the materials.
4. Plastics and Polymers
Ribbon blenders are used in the plastics sector for dry blending resins, stabilizers, and additives before further processing like extrusion or molding.
Materials include:
Thermoplastic powders
Color masterbatches and pigments
Plasticizers and fillers
Flame retardants and UV stabilizers
Consistent dispersion of colorants or performance modifiers is critical to achieving uniform properties in the final plastic product.
5. Construction Materials
In construction and building materials, ribbon blenders mix dry and semi-moist materials needed for coatings, mortars, and other structural compounds.
Examples include:
Tile adhesives and grout powders
Dry cement or mortar mixtures
Insulating materials
Wall plasters and putty
Epoxy and resin-based compounds
The blender may be integrated with feeding and bagging systems to streamline batch production.
6. Cosmetics and Personal Care
The cosmetic industry also utilizes ribbon blenders to mix powders and creams in small- to medium-scale production.
Processed ingredients include:
Face powders and foundation bases
Talc and mica blends
Bath salts and exfoliants
Skincare base creams (in modified ribbon mixers with thicker paddles)
Hair care powder products
Hygienic construction and non-contaminating surfaces are critical for personal care applications.
7. Agricultural and Animal Feed
Ribbon blenders are effective for processing animal feed premixes, agricultural chemicals, and supplements.
Materials include:
Vitamin and mineral feed blends
Grain powders and mash
Pesticide powders
Crop nutrient formulations
Dry pet food additives
These products often require accurate ingredient dosing to ensure consistency and safety in animal nutrition.
Conclusion
The ribbon blender's flexible and efficient mixing mechanism makes it suitable for a wide range of materials, from fine pharmaceutical powders to industrial chemicals and food-grade powders. When selecting a ribbon blender for a specific material, considerations such as bulk density, flow characteristics, particle size, moisture content, and regulatory requirements will help determine the right machine design and configuration.



 Español
Español