A tray dryer is a batch drying equipment widely used in the pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries for removing moisture from solid materials. It provides uniform drying performance through controlled air circulation and temperature regulation. This article explores its structure, working principle, design configurations, and practical use to help users choose and operate a tray dryer effectively.
Content
1. Structure and Working Principle of a Tray Dryer
The tray dryer consists of an insulated chamber with multiple trays arranged in tiers, a heat source, and a fan system for air circulation. The material to be dried is spread evenly on the trays, and hot air passes through or around them to evaporate moisture efficiently.
1.1 Air Circulation Mechanism
Hot air is circulated through a fan that ensures uniform heat distribution throughout the chamber. The air may flow horizontally or vertically depending on the design. Uniform airflow is crucial to maintain consistent drying quality across all trays.
1.2 Heating Methods
Heating sources typically include steam, electricity, or hot water. The choice of heating method depends on the product type and required temperature control. Steam-heated dryers are common in industrial settings for energy efficiency, while electric models are used for laboratory or small-scale production.
2. Design Features and Performance Parameters
Tray dryers are designed to maintain high thermal efficiency, easy operation, and simple cleaning. The key design parameters include air velocity, tray spacing, drying temperature, and exhaust humidity control.
| Feature | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Adjustable according to material type | 40°C – 150°C |
| Air Circulation Type | Forced convection via motorized fan | Horizontal or vertical |
| Drying Uniformity | Variation in moisture content after drying | ±2% typical |
3. Material Handling and Loading Techniques
The efficiency of drying depends largely on how the material is prepared and loaded. The layer thickness should be uniform across trays to promote even moisture removal. Overloading can restrict airflow and result in uneven drying.
- Spread materials in thin, uniform layers to improve air contact.
- Avoid stacking or clumping materials that may block airflow.
- Use stainless steel trays for corrosion resistance and easy cleaning.
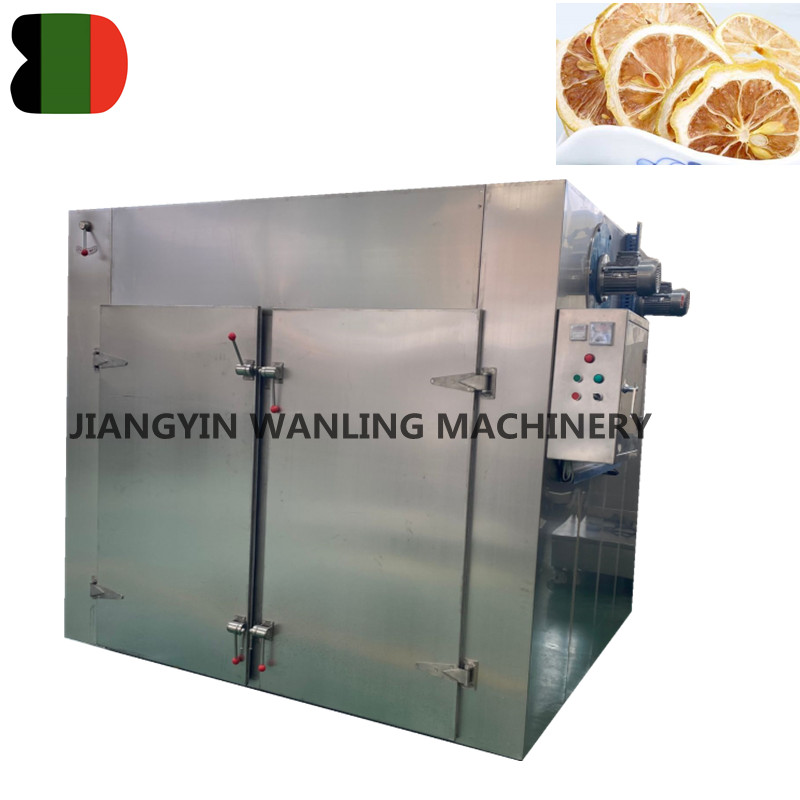

4. Applications of Tray Dryers in Various Industries
Tray dryers are used in many industries because they allow precise temperature control and are suitable for heat-sensitive products. The main applications include:
- Pharmaceutical industry: Drying powders, granules, and tablets at controlled temperatures without contamination.
- Food processing: Dehydrating fruits, vegetables, spices, and herbs while preserving color and flavor.
- Chemical manufacturing: Drying catalysts, pigments, and polymers that require uniform moisture removal.
- Textile and dyeing: Removing moisture from treated fabrics and dye intermediates.
5. Maintenance and Safety Guidelines
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of a tray dryer and prevents operational issues. Regular cleaning, inspection, and calibration help maintain efficiency and product quality.
5.1 Routine Maintenance Tasks
- Clean trays and chamber surfaces after each batch to avoid cross-contamination.
- Inspect fan blades and filters for dust buildup or imbalance.
- Check temperature sensors and controllers for calibration drift.
5.2 Safety Considerations
- Do not exceed maximum rated temperature or load capacity.
- Ensure proper ventilation to avoid heat accumulation and potential fire hazards.
- Use heat-resistant gloves when handling trays or loading materials.
6. Advantages of Using a Tray Dryer
Tray dryers are preferred for their versatility and ease of control. They can handle small to medium-scale production with predictable performance. Below are key benefits:
- Uniform drying with controllable airflow and temperature.
- Suitable for a wide range of materials and industries.
- Ease of operation, cleaning, and maintenance.
- Energy-efficient designs available with heat recovery systems.
A tray dryer remains one of the most practical drying solutions for batch operations that require precision and cleanliness. Its flexibility and reliability make it a cornerstone in many industrial drying processes.


 Español
Español