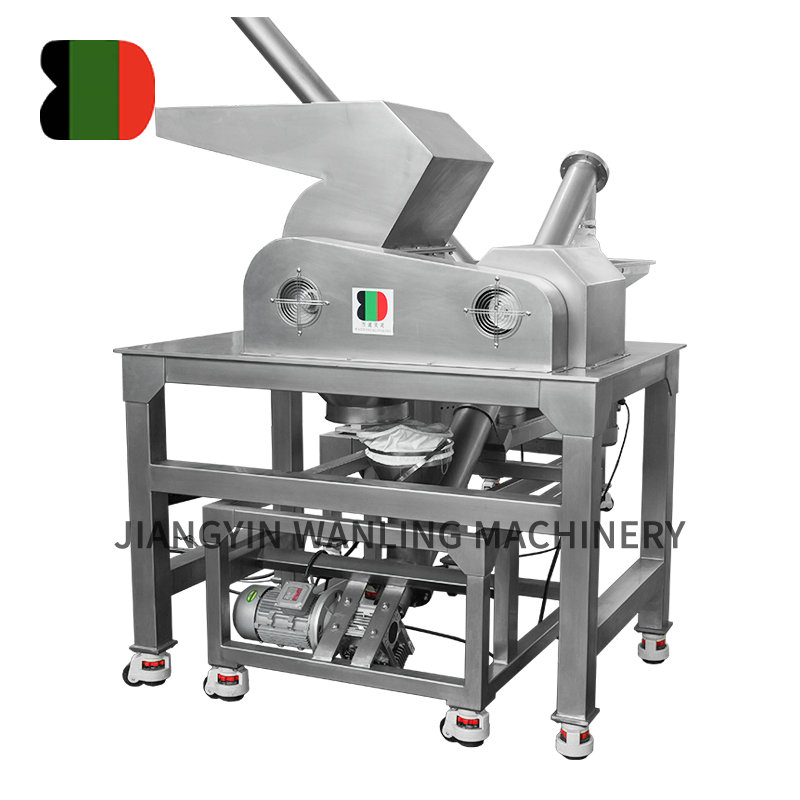
Granulation plays a crucial role in various industries, particularly in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. The granulation process improves powder flow, compressibility, and uniformity of the end product. Two of the most commonly used granulation machines are the High Shear Mixer Granulator (HSMG) and the Rapid Mixer Granulator (RMG). While both machines are designed to achieve granulation, they differ in structure, operation, and specific application suitability. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between these two types of granulators to help professionals make informed decisions about their use.
What is a High Shear Mixer Granulator?
A High Shear Mixer Granulator is a granulation machine that primarily operates using a high-speed impeller and chopper to mix powders and liquids intensively. The "high shear" refers to the intense mechanical forces applied to the materials, which results in the rapid formation of dense, uniform granules. The high shear action ensures thorough wetting of powders and efficient particle bonding.
Key Features of High Shear Mixer Granulator:
High-speed mixing and chopper blades that generate intense mechanical shear.
Ability to handle high-viscosity binders or sticky powders.
Produces relatively dense, spherical granules with good mechanical strength.
Typically used in wet granulation processes.
What is a Rapid Mixer Granulator?
Rapid Mixer Granulators, also known as Fluid Bed Granulators in some contexts, combine fast mixing action with controlled addition of binding agents. The term "rapid" highlights the swift and efficient mixing process, but the shear forces are generally lower compared to high shear granulators. Rapid mixers use a combination of a high-speed impeller and a low-speed chopper to ensure even distribution of liquids and uniform granule formation.
Key Features of Rapid Mixer Granulator:
Quick blending of powders and liquid binders.
Less intense shear forces compared to HSMG.
Typically produces porous, less dense granules.
Widely used in pharmaceutical tablet production and other industries requiring uniform granule size distribution.
Core Differences Between High Shear Mixer Granulator and Rapid Mixer Granulator
| Aspect | High Shear Mixer Granulator | Rapid Mixer Granulator |
|---|---|---|
| Shear Force | High shear due to fast impeller and chopper | Moderate shear with less aggressive mixing |
| Granule Density | Denser, more compact granules | More porous and less dense granules |
| Mixing Speed | High-speed mixing with intense energy input | Rapid mixing with controlled energy |
| Typical Granule Shape | Spherical and smooth granules | Irregular, porous granules |
| Suitable Powders | Sticky, high-viscosity powders | Free-flowing powders |
| Common Applications | Wet granulation in pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals | Pharmaceutical tablets, some food processing |
| Binder Addition | Usually added gradually with continuous mixing | Evenly distributed binder with fast mixing |
Applications and Industry Uses
Both types of granulators serve crucial roles in product formulation, especially in pharmaceutical manufacturing where granule quality directly affects tablet quality. High shear mixer granulators are preferred when granules with higher mechanical strength are needed or when working with challenging formulations that require intensive mixing. On the other hand, rapid mixer granulators offer faster processing times and better control over granule size distribution, which is important for certain tablet compression processes.

Choosing between a high shear mixer granulator and a rapid mixer granulator depends largely on the material characteristics, required granule properties, and production scale. Understanding their operational differences and performance attributes is essential for optimizing the granulation process and ensuring product quality. While both machines are valuable tools in powder processing, aligning the granulator type with the specific production needs can enhance efficiency, reduce processing time, and improve overall product consistency.


 Español
Español